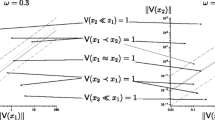
Abstract
Topological predicates are an important element of database systems that allow manipulation of spatial data. Based on the necessity for such systems to handle uncertainty, we introduce a general mechanism that identifies vague topological predicates. This definition forms part of a formal data model referred to as VASA (Vague Spatial Algebra), in which the data types vague regions, vague lines, and vague points are defined in terms of existing definition of crisp spatial data types. Following this trend, the mechanism presented here identifies vague topological predicates on the basis of well defined crisp topological predicates. An example implementation of the mechanism for vague regions is given.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui, Z., Cohn, A.G., Randell, D.A.: Qualitative and Topological Relationships. In: Abel, D.J., Ooi, B.-C. (eds.) SSD 1993. LNCS, vol. 692, pp. 296–315. Springer, Heidelberg (1993)
Burrough, P.A., Frank, A.U. (eds.): Geographic Objects with Indeterminate Boundaries. GISDATA Series, vol. 2. Taylor & Francis, Abington (1996)
Egenhofer, M.J., Clementini, E., Di Felice, P.: Topological Relations between Regions with Holes. Int. Journal of Geographical Information Systems 8(2), 128–142 (1994)
Egenhofer, M.J., Herring, J.: Categorizing Binary Topological Relations Between Regions, Lines, and Points in Geographic Databases. Technical Report 90-12, National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis, University of California, Santa Barbara (1990)
Pauly, A., Schneider, M.: Vague Spatial Data Types, Set Operations, and Predicates. In: Benczúr, A.A., Demetrovics, J., Gottlob, G. (eds.) ADBIS 2004. LNCS, vol. 3255, pp. 379–392. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Pauly, A., Schneider, M.: Identifying Topological Predicates for Vague Spatial Objects. In: 20th ACM Symp. for Applied Computing, pp. 587–591 (2005)
Erwig, M., Schneider, M.: Vague Regions. In: Scholl, M.O., Voisard, A. (eds.) SSD 1997. LNCS, vol. 1262, pp. 298–320. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Behr, T., Schneider, M.: Topological Relationships of Complex Points and Complex Regions. In: Int. Conf. on Conceptual Modeling, pp. 56–69 (2001)
Cohn, A.G., Gotts, N.M.: The ‘Egg-Yolk’ Representation of Regions with Indeterminate Boundaries. In: Frank, A.U. (ed.) [2], pp. 171–187 (1996)
Clementini, E., Di Felice, P.: An Algebraic Model for Spatial Objects with Indeterminate Boundaries. In: Frank, A.U. (ed.) [2], pp. 153–169 (1996)
Clementini, E., Di Felice, P., Califano, G.: Composite Regions in Topological Queries. Information Systems 20(7), 579–594 (1995)
Egenhofer, M.J., Franzosa, R.D.: Point-Set Topological Spatial Relations. Int. Journal of Geographical Information Systems 5(2), 161–174 (1991)
Schneider, M., Behr, T.: Topological Relationships between Complex Spatial Objects. Technical Report, CISE Dept., University of Florida (2004)
Schneider, M.: Spatial Data Types for Database Systems. LNCS, vol. 1288. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Schneider, M.: Uncertainty Management for Spatial Data in Databases: Fuzzy Spatial Data Types. In: Güting, R.H., Papadias, D., Lochovsky, F.H. (eds.) SSD 1999. LNCS, vol. 1651, pp. 330–351. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Worboys, M.: Computation with Imprecise Geospatial Data. Computational, Environmental and Urban Systems 22(2), 85–106 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pauly, A., Schneider, M. (2005). Topological Predicates Between Vague Spatial Objects. In: Bauzer Medeiros, C., Egenhofer, M.J., Bertino, E. (eds) Advances in Spatial and Temporal Databases. SSTD 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3633. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11535331_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11535331_24
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-28127-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31904-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)