Abstract
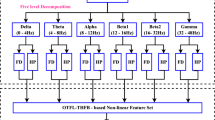
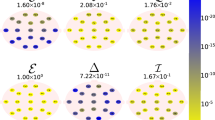
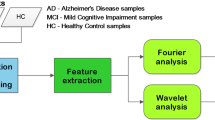
The early detection Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an important challenge. In this paper, we propose a novel method for early detection of AD using electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings: first a blind source separation algorithm is applied to extract the most significant spatio-temporal components; these components are subsequently wavelet transformed; the resulting time-frequency representation is approximated by sparse “bump modeling”; finally, reliable and discriminant features are selected by orthogonal forward regression and the random probe method. These features are fed to a simple neural network classifier. The method was applied to EEG recorded in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) who later developed AD, and in age-matched controls. This method leads to a substantially improved performance (93% correctly classified, with improved sensitivity and specificity) over classification results previously published on the same set of data. The method is expected to be applicable to a wide variety of EEG classification problems.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Musha, T., Asada, T., Yamashita, F., Kinoshita, T., Chen, Z., Matsuda, H., Masatake, U., Shankle, W.R.: A new EEG method for estimating cortical neuronal impairment that is sensitive to early stage Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical Neurophysiology 113(7), 1052–1058 (2002)
Jeong, J.: EEG dynamics in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical Neurophysiology 115, 1490–1505 (2004)
DeKosky, S.T., Marek, K.: Looking backward to move forward: early detection of neurodegenerative disorders. Science 302(5646), 830–834 (2003)
Nestor, P.J., Scheltens, P., Hodges, J.R.: Advances in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine 10(suppl.), S34–41 (2004) Review
Cichocki, A., Shishkin, S.L., Musha, T., Leonowicz, Z., Asada, T., Kurachi, T.: EEG filtering based on blind source separation (BSS) for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical Neurophysiology 116(3), 729–737 (2005)
Cichocki, A.: Blind Signal Processing Methods for Analyzing Multichannel Brain Signals. International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism 6(1) (2004)
Cichocki, A., Amari, S.: Adaptative Blind Signal and Image Processing: Learning Algorithms and Applications. Wiley, New York (2003)
Tong, L., Soon, V., Huang, Y.F., Liu, R.: Indeterminacy and identifiability of blind identification. IEEE Transactions CAS 38, 499–509 (1991)
Tong, L., Inouye, Y., Liu, R.: Waveform-preserving blind estimation of multiple independent sources. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 41(7), 2461–2470 (1993)
Szupiluk, R., Cichocki, A.: Blind signal separation using second order statistics. In: Proceedings of SPETO, pp. 485–488 (2001)
Cichocki, A., Amari, S., Siwek, K., Tanaka, T., et al.: ICALAB toolboxes. Available online at http://www.bsp.brain.riken.jp/ICALAB
Vialatte, F., Martin, C., Dubois, R., Quenet, B., Gervais, R., Dreyfus, G.: A machine learning approach to the analysis of time-frequency maps, and its application to neural dynamics. Neural Networks (submitted)
Poularikas, A.D.: The transforms and applications handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1996)
Kronland-Martinet, R., Morlet, J., Grossmann, A.: The wavelet Transform. In: Chen, C.H. (ed.) Expert Systems and Pattern Analysis, pp. 97–126. World Scientific, Singapore (1987)
Tallon-Baudry, C., Bertrand, O., Delpuech, C., Pernier, J.: Stimulus specificity of phase-locked and non-phase-locked 40 Hz visual responses in human. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 4240–4249 (1996)
Ohara, S., Crone, N.E., Weiss, N., Lenz, F.A.: Attention to a painful cutaneous laser stimulus modulates electrocorticographic event-related desychronization in humans. Clinical Neurophysiology 115, 1641–1652 (2004)
Caplan, J.B., Madsen, J.R., Raghavachari, S., Kahana, M.J.: Distinct patterns of brain oscillations underlie two basic parameters of human maze learning. Journal of Neurophysiology 86, 368–380 (2001)
Düzel, E., Habib, R., Schott, B., Schoenfeld, A., Lobaugh, N., McIntosh, A.R., Scholz, M., Heinze, H.J.: A multivariate, spatiotemporal analysis of electromagnetic time-frequency data of recognition memory. Neuroimage 18, 185–197 (2003)
Dubois, R.: Application de nouvelles méthodes d’apprentissage à la détection précoce d’anomalies en électrocardiographie. PhD thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie - Paris VI (2004), Available from http://www.neurones.espci.fr/Francais.Docs/dossier_recherche/bibliographie/theses_soutenues.htm#ancre41560
Dubois, R., Quenet, B., Faisandier, Y., Dreyfus, G.: Building meaningful representations in knowledge-driven nonlinear modeling. Neurocomputing (2005) (in print)
Vialatte, F., Martin, C., Ravel, N., Quenet, B., Dreyfus, G., Gervais, R.: Oscillatory activity, behaviour and memory, new approaches for LFP signal analysis. 35th annual general meeting of the European brain and behaviour society, 17-20 September 2003, Barcelona, Spain – Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis 63(suppl.) (2003)
Press, W.H., Flannery, B.P., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T.: Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, pp. 425–430. Cambridge Univ. Press, New York (1992)
Guyon, I., Elisseef, A.: An Introduction to Variable and Feature Selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research 3, 1157–1182 (2003)
Chen, S., Billings, S.A., Luo, W.: Orthogonal least squares methods and their application to non-linear system identification. International Journal of Control 50, 1873–1896 (1989)
Jong, K., Marchiori, E., Sebag, M.: Ensemble Learning with Evolutionary Computation: Application to Feature Ranking. In: Gelbukh, A. (ed.) CICLing 2001. LNCS, vol. 2004, pp. 1133–1142. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Stoppiglia, H., Dreyfus, G., Dubois, R., Oussar, Y.: Ranking a Random Feature for Variable and Feature Selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research 3, 1399–1414 (2003)
Haykin, S.: Neural Networks – a comprehensive foundation, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1999)
Stone, M.: Cross-validatory choice and assessment of statistical predictions (with discussion). Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B 36, 111–147 (1974)
Klimesch, W.: EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: a review and analysis. Brain Research Reviews 29, 169–195 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Dreyfus, G., Musha, T., Shishkin, S.L., Gervais, R. (2005). Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease by Blind Source Separation, Time Frequency Representation, and Bump Modeling of EEG Signals. In: Duch, W., Kacprzyk, J., Oja, E., Zadrożny, S. (eds) Artificial Neural Networks: Biological Inspirations – ICANN 2005. ICANN 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3696. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11550822_106
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11550822_106
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-28752-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-28754-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)