Abstract
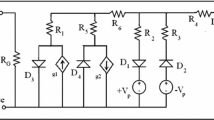
In this paper, we present a model, Internode, that unifies the gate functional behavior and the dynamic one. It is based on a FSM that represents the internal state of the gate depending on the electrical load of its internal nodes allowing to consider aspects like input collisions and internal power consumption. Also, we explain the importance of internal power consumption (such effect occurs when an input transition does not affect the output) in three different technologies (AMS 0.6 μm, AMS 0.35 μm, and UMC 130 nm). This consumption becomes more remarkable as technology advances yielding to underestimating up to 9.4% of global power consumption in the UMC 130 nm case. Finally, we show how to optimize power estimation in the SCMOS NOR-2 gate by applying Internode to modeling its consumption accurately.
This work has been partially supported by the MEC META project TEC 2004-00840/MIC of the Spanish Government
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuroda, T.: Low-voltage technologies and circuits. In: Chandrakasan, A., B.R. (eds.) Low-power CMOS design, pp. 61–65. Wiley-IEEE Press, New York, NY, USA (1998)
Daga, J.M., Auvergne, D.: A comprehensive delay macromodeling for submicrometer CMOS logics. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 34(1), 42–55 (1999)
Kayssi, A.I., Sakallah, K.A., Mudge, T.N.: The impact of signal transition time on path delay computation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing 40(5), 302–309 (1993)
Chandrakasan, A., Sheng, S., B.R.: Low-power CMOS digital design. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 27(4), 473–484 (1992)
Millan, A., Bellido, M.J., Juan, J., Guerrero, D., Ruiz-de Clavijo, P., Ostua, E.: Internode: Internal node logic computational model. In: Proc. 36th Annual Simulation Symposium (part of the Advanced Simulation Technologies Conference, ASTC), Orlando, Florida, USA, March 2003, pp. 241–248. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2003)
Moore, E.F.: Gedanken experiments on sequential machines. In: Automata Studies, pp. 129–153. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1956)
Bisdounis, L., Koufopavlou, O.: Analytical modeling of short-circuit energy dissipation in submicron CMOS structures. In: Proc. 6th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), September 1999, pp. 1667–1670 (1999)
Maurine, P., Azemard, N., Auvergne, D.: Structure independent representation of output transition time for CMOS library. In: Hochet, B., Acosta, A.J., Bellido, M.J. (eds.) PATMOS 2002. LNCS, vol. 2451, pp. 247–257. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Nabavi-Lishi, A., Rumin, N.C.: Inverter models of CMOS gates for supply current and delay evaluation. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 13, 1271–1279 (1994)
Najm, F.N.: A survey of power estimation techniques in vlsi circuits. IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems 2(4), 446–455 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Millán Calderón, A. et al. (2005). Application of Internode Model to Global Power Consumption Estimation in SCMOS Gates. In: Paliouras, V., Vounckx, J., Verkest, D. (eds) Integrated Circuit and System Design. Power and Timing Modeling, Optimization and Simulation. PATMOS 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3728. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11556930_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11556930_35
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29013-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32080-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)