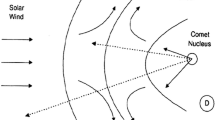
Abstract
Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) models of plasma can be used to model many phenomena in the solar system. In this work we investigate the use of a general MHD solver – the Flash code – for the simulation of the interaction between the solar wind and solar system objects. As a test case we simulate the three-dimensional solar wind interaction with a simplified model of a comet and describe the modifications of the code. The simulation results are found to be consistent with previously published ones. We investigate the performance of the code by varying the number of processors and the number of grid cells. The code is found to scale well. Finally we outline how to simulate the solar wind interaction with other objects using the Flash code.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alliances Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes (ASCI), http://flash.uchicago.edu
Kivelson, M.G., Russell, C.T. (eds.): Introduction to Space Physics. University Press, Cambridge (1995) ISBN 0 521 45104 4
Priest, E.R., Hood, A.W. (eds.): Advances in Solar System Magnetohydrodynamics. University Press, Cambridge (1991) ISBN 0 521 40325 1
Matsumoto, H., Omura, Y. (eds.): Computer Space Plasma Physics. Terra Scientific Publishing Company, Tokyo (1993) ISBN 4 88704 111 X
Kabin, K., Hansen, K.C., Gombosi, T.I., Combi, M.R., Linde, T.J., DeZeeuw, D.L., Groth, C.P.T., Powell, K.G., Nagy, A.F.: Global MHD simulations of space plasma environments: heliosphere, comets, magnetospheres of planets and satellites. Astrophysics and Space Science 274, 407–421 (2000)
Ogino, T., Walker, R.J., Ashour-Abdalla, M.: A Three-Dimensional MHD Simulation of the Interaction of the Solar Wind With Comet Halley. Journal of Geophysical Research 93(A9), 9568–9576 (1988)
Gombosi, T.I., De Zeeuw, D.L., Häberli, R.M., Powell, K.G.: Three-dimensional multiscale MHD model of cometary plasma environments. Journal of Geophysical Research 101(A7), 15232–15233 (1996)
Gombosi, T.I.: Physics of the Space Environment. University Press, Cambridge (1998) ISBN 0 521 59264 X
The Message Passing Interface (MPI), http://www-unix.mcs.anl.gov/mpi/
Parallel Adaptive Mesh Refinement (PARAMESH), http://ct.gsfc.nasa.gov/paramesh/Users_manual/amr.html
MacNeice, P., Olson, K.M., Mobarry, C., de Fainchtein, R., Packer, C.: PARAMESH: A parallel adaptive mesh refinement community toolkit. Computer Physics Communications 126, 330–354 (2000)
Schmidt, H.U., Wegmann, R.: Plasma flow and magnetic fields in comets Comets: Gases. In: Wilkening, L.L. (ed.) Ices,Grains and Plasma, University of Arizona Press, Tuscon
High Performance Computing Center North, Umeå, Sweden, http://www.hpc2n.umu.se
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ekenbäck, A., Holmström, M. (2006). MHD Modeling of the Interaction Between the Solar Wind and Solar System Objects. In: Dongarra, J., Madsen, K., Waśniewski, J. (eds) Applied Parallel Computing. State of the Art in Scientific Computing. PARA 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3732. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11558958_66
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11558958_66
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29067-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-33498-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)