Abstract
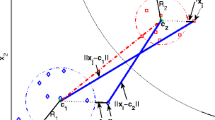
Previous sphere-based classification algorithms usually need a number of spheres in order to achieve good classification performance. In this paper, inspired by the support vector machines for classification and the support vector data description method, we present a new method for constructing single spheres that separate data with the maximum separation ratio. In contrast to previous methods that construct spheres in the input space, the new method constructs separating spheres in the feature space induced by the kernel. As a consequence, the new method is able to construct a single sphere in the feature space to separate patterns that would otherwise be inseparable when using a sphere in the input space. In addition, by adjusting the ratio of the radius of the sphere to the separation margin, it can provide a series of solutions ranging from spherical to linear decision boundaries, effectively encompassing both the support vector machines for classification and the support vector data description method. Experimental results show that the new method performs well on both artificial and real-world datasets.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, P.W.: The hypersphere in pattern recognition. Information and Control 5, 324–346 (1962)
Cooper, P.W.: Note on adaptive hypersphere decision boundary. IEEE Transactions on Electronic Computers, 948–949 (1966)
Batchelor, B.G., Wilkins, B.R.: Adaptive discriminant functions. Pattern Recognition 42, 168–178 (1968)
Batchelor, B.G.: Practical Approach to Pattern Classification. Plenum, New York (1974)
Reilly, D.L., Cooper, L.N., Elbaum, C.: A neural model for category learning. Biological Cybernetics 45, 35–41 (1982)
Scofield, C.L., Reilly, D.L., Elbaum, C., Cooper, L.N.: Pattern class degeneracy in an unrestricted storage density memory. In: Anderson, D.Z. (ed.) Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 674–682. American Institute of Physics, Denver (1987)
Marchand, M., Shawe-Taylor, J.: The set covering machine. Journal of Machine Learning Research 3, 723–746 (2002)
Boser, B.E., Guyon, I.M., Vapnik, V.N.: A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: Haussler, D. (ed.) Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, pp. 144–152 (1992)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.N.: Support vector networks. Machine Learning 20, 273–297 (1995)
Vapnik, V.N.: Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York (1998)
Schölkopf, B., Burges, C., Vapnik, V.: Extracting support data for a given task. In: Proceedings of First International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 252–257 (1995)
Tax, D.M.J., Duin, R.P.W.: Data domain description by support vectors. In: Verleysen, M., ed.: Proceedings ESANN, Brussels, pp. 251–256. D. Facto Press (1999)
Platt, J.: Fast training of support vector machines using sequential minimal optimization. In: Schölkopf, B., Burges, C.J.C., Smola, A.J. (eds.) Advances in Kernel Methods - Support Vector Learning, pp. 185–208. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Vapnik, V.N.: Estimation of Dependence Based on Empirical Data. Springer, Berlin (1982)
Osuna, E., Freund, R., Girosi, R.: Support vector machines: training and applications. A.I. Memo AIM - 1602. MIT A.I. Lab (1996)
Glineur, F.: Pattern separation via ellipsoids and conic programming, Mémoire de D.E.A., Faculté Polytechnique de Mons, Mons, Belgium (September 1998)
Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Shawe-Taylor, J., Smola, A.J.: Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation 13, 1443–1471 (2001)
Blake, C., Merz, C.: UCI repository of machine learning databases (1998), http://www.ics.uci.edu/~mlearn/MLRepository.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, J., Neskovic, P., Cooper, L.N. (2005). Pattern Classification via Single Spheres. In: Hoffmann, A., Motoda, H., Scheffer, T. (eds) Discovery Science. DS 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3735. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11563983_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11563983_21
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29230-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31698-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)