Abstract
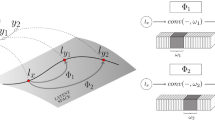
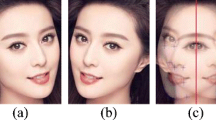
Pose variations, especially large out-of-plane rotations, make face recognition a difficult problem. In this paper, we propose an algorithm that uses a single input image to accurately synthesize an image of the person in a different pose. We represent the two poses by stacking their information (pixels or feature locations) in a combined feature space. A given test vector will consist of a known part corresponding to the input image and a missing part corresponding to the synthesized image. We then solve for the missing part by maximizing the test vector’s probability. This approach combines the “distance-from-feature-space” and “distance-in-feature-space”, and maximizes the test vector’s probability by minimizing a weighted sum of these two distances. Our approach does not require either 3D training data or a 3D model, and does not require correspondence between different poses. The algorithm is computationally efficient, and only takes 4 – 5 seconds to generate a face. Experimental results show that our approach produces more accurate results than the commonly used linear-object-class approach. Such technique can help face recognition to overcome the pose variation problem.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, M., Jepson, A.: Eigen-tracking: Robust matching and tracking of articulated objects using a view-based representation. International Journal of Computer Vision 36(2), 101–130 (1998)
Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: A Morphable Model for the Synthesis of 3D Faces. ACM Siggraph (1999)
Blanz, V., Vetter, T.: Face Recognition Based on Fitting a 3D Morphable Model. IEEE TPAMI 25(9), 1063–1074 (2003)
Blanz, V., Grother, P., Phillips, P.J., Vetter, T.: Face Recognition Based on Frontal Views generated from Non-Frontal Images. In: CVPR (2005)
Cootes, T.F., Edwards, G.J., Taylor, C.J.: Active Appearance Models. IEEE TPAMI 23(6), 681–685 (2001)
Debevec, P., Taylor, C., Malik, J.: Modeling and rendering architecture from photographs: A hybrid geometry- and image-based approach. In: Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH), pp. 11–20 (1996)
Gross, R., Matthews, I., Baker, S.: Appearance-Based Face Recognition and Light-Fields. IEEE TPAMI 26(4), 449–465 (2004)
Hwang, B.-W., Lee, S.-W.: Reconstruction of Partially Damaged Face Images Based on a Morphable Face Model. IEEE TPAMI 25(3), 365–372 (2003)
Leonardis, A., Bischof, H.: Robust recognition using eigenimages. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 78(1), 99–118 (2000)
Moghaddam, B., Pentland, A.: Probabilistic Visual Learning for Object Representation. IEEE TPAMI 19(7), 696–710 (1997)
Sim, T., Baker, S., Bsat, M.: The CMU Pose, Illumination, and Expression Database. IEEE TPAMI 25(12), 1615–1618 (2003)
Vetter, T., Poggio, T.: linear object classes and Image Synthesis From a Single Example Image. IEEE TPAMI 19(7), 733–742 (1997)
Xiao, J.: Reconstruction, Registration, and Modeling of Deformable Object Shapes. CMU RI PhD thesis (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ni, J., Schneiderman, H. (2005). Face View Synthesis Across Large Angles. In: Zhao, W., Gong, S., Tang, X. (eds) Analysis and Modelling of Faces and Gestures. AMFG 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3723. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11564386_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11564386_28
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29229-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32074-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)