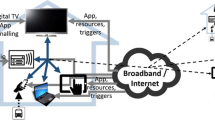
Abstract
In order to adapt content delivery to different client capabilities and preferences, we propose a content selection model to automatically classify HTML content based on its functionality, then map client descriptions on preferences and device capabilities into our classification scheme, and finally selectively deliver the content which users want and which devices can handle. The experiment shows that our content selection model could reduce HTML object size, object latency and page latency. Therefore, it is effective in saving network resources and improving clients’ access experiences.
This research is supported by the funding 2004CB719400 of China.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra, S., Ellis, C.S.: JPEG Compression Metric as a Quality Aware Image Transcoding. In: Proceedings of the 2nd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems (1999)
ClickZ Internet Statistics and Demographics, http://www.clickz.com/stats/
Composite Capability and Preference Profile, http://www.w3.org/Mobile/CCPP/
ESI language specification 1.0 (2000), http://www.esi.org
Fox, S.D., Gribble, E.A.: Adapting to Network and Client Variability via On-Demand Dynamic Distillation. In: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, ASPLOS (1996)
Hori, M., Kondoh, G., Ono, K., Hirose, S., Singhal, S.: Annotation-Based Web Content Transcoding. In: Proceedings of The 9th WWW Conference (2000)
Internet Content Adaptation Protocol (I-CAP), http://www.i-cap.org
IRCACHE Proxy Traces, http://ircache.nlanr.net
Knutsson, B., Lu, H.H., Mogul, J.C.: Architecture and pragmatics of Server directed transcoding. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Web Content Caching and Distribution (2002)
Mogul, J.C.: Server Directed Transcoding. Computer Communications 24(2), 155–162 (2001)
Mohan, R., Smith, J.R., Li, C.S.: Adapting Multimedia Internet Content for Universal Access. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 1(1), 104–114 (1999)
Open Pluggable Edge Service (OPES), http://www.ietf-opes.org
Smith, J.R., Mohan, R., Li, C.S.: Transcoding Internet Content for Hetero-geneous Client Devices. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS (1998)
Spyglass-Prism, http://www.opentv.com/support/primer/prism.htm
User Agent Profile, WAP forum, http://www.wapforum.org/what/technical/SPEC-UAProf-19991110.pdf
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ding, C., Zhang, S., Chi, CH. (2005). Content Selection Model for Adaptive Content Delivery. In: Cao, J., Nejdl, W., Xu, M. (eds) Advanced Parallel Processing Technologies. APPT 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3756. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11573937_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11573937_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29639-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32107-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)