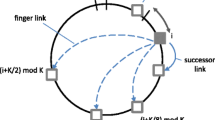
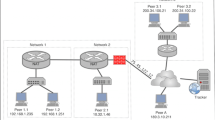
Abstract
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks have proved to be a powerful and highly scalable alternative to traditional client-server architectures for content distribution. They offer the technical means to efficiently distribute data to millions of clients simultaneously with very low infrastructural cost. Previous studies of content distribution architectures have primarily focused on homogeneous systems where the bandwidth capacities of all peers are similar, or simple heterogeneous scenarios where different classes of peers with symmetric bandwidth try to minimize the average download duration. In this paper, we study the problem of content distribution under the assumption that peers have heterogeneous and asymmetric bandwidth (typical for ADSL connections), with the objective to provide uniform download rates to all peers—a desirable property for distributing streaming content. We discuss architectures that fulfill this goal and achieve optimal utilization of the aggregate uplink capacity of the peers. We develop analytical models that provide insight on their performance in various configurations, and we compare them to architectures with non-uniform rates. Our results indicate that heterogeneous and asymmetric peers can achieve uniform download rates with little additional complexity and no performance penalty.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, Y., Rao, S., Zhang, H.: A case for end system multicast. In: Proceedings of ACM Sigmetrics (2000)
Hefeeda, M., Habib, A., Boyan, B., Xu, D., Bhargava, B.: PROMISE: peer-to-peer media streaming using CollectCast. Technical Report CS-TR 03-016, Purdue University (2003)
Jiang, X., Dong, Y., Xu, D., Bhargava, B.: Gnustream: A P2P media streaming system prototype. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, ICME (2003)
Chawathe, Y.: Scattercast: An adaptable broadcast distribution framework. Multimedia Systems 9, 104–118 (2003)
Castro, M., Druschel, P., Kermarrec, A.-M., Nandi, A., Rowstron, A., Singh, A.: SplitStream: High-bandwidth multicast in a cooperative environment. In: Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, SOSP (2003)
Jannotti, J., Gifford, D., Johnson, K.L., Kaashoek, M.F., O’Toole, J.W.: Overcast: Reliable multicasting with an overlay network. In: Proceedings of the 4th Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation, OSDI (2000)
Pendarakis, D., Shi, S., Verma, D., Waldvogel, M.: Almi: An application level multicast infrastructure. In: Proceedings of USITS (2001)
Padmanabhan, V., Wang, H., Chou, P.: Resilient peer-to-peer streaming. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICNP (2003)
Rao, S., Padmanabhan, V., Seshan, S., Zhang, H.: The impact of heterogeneous bandwidth constraints on dht-based multicast protocols. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on P2P Systems (IPTPS) (2005)
Castro, M., Druschel, P., Kermarrec, A.M., Rowstron, A.: Scribe: a large-scale and decentralized application-level Multicast infrastructure. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 20, 1489–1499 (2003)
Biersack, E., Rodriguez, P., Felber, P.: Performance analysis of peer-to-peer networks for file distribution. In: Solé-Pareta, J., Smirnov, M., Van Mieghem, P., Domingo-Pascual, J., Monteiro, E., Reichl, P., Stiller, B., Gibbens, R.J. (eds.) QofIS 2004. LNCS, vol. 3266, pp. 1–10. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Yang, X., de Veciana, G.: Service capacity of peer-to-peer networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM (2004)
Carra, D., Cigno, R.L., Biersack, E.: Introducing heterogeneity in performance analysis of p2p networks for file distribution. Technical Report DIT-04-113, University of Trento (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Schiely, M., Felber, P. (2005). Peer-to-Peer Distribution Architectures Providing Uniform Download Rates. In: Meersman, R., Tari, Z. (eds) On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems 2005: CoopIS, DOA, and ODBASE. OTM 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3761. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11575801_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11575801_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29738-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32120-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)