Abstract
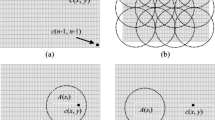
Recent researches on energy efficient coverage configuration in wireless sensor networks mainly address the goal of 100% or near 100% coverage preserving. However, we find that a small percentage of loss of coverage, which is acceptable in many applications, can result in dramatic increase in energy savings. Therefore, in this paper percentage coverage rather than complete coverage is selected as the design goal, and a location-based Percentage Coverage Configuration Protocol (PCCP) is developed to assure that the proportion of the sensing area after configuration to the original sensing area is no less than a desired percentage. Numerical testing results show that PCCP can not only guarantee the desired coverage percentage but also generate more energy efficient configuration in comparison with the existing schemes so that the system lifespan is extended significantly.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurenhammer, F.: Voronoi Diagrams – A Survey of a Fundamental Geometric Data Structure. ACM Computing Surveys 23(3), 345–405 (1991)
Cardei, M., Wu, J.: Energy-Efficient Coverage Problems in Wireless Ad Hoc Sensor Networks. Accepted to appear in Special Issue of the Journal of Computer Communications on Sensor Networks, This paper can be got from the following link: http://polaris.cse.fau.edu/~jie/research/publications/Publication_files/coverage.pdf
Hsin, C., Liu, M.: Network Coverage Using Low Duty-Cycled Sensors: Random & Coordinated Sleep Algorithms. In: IPSN 2004, Berkeley, California, USA, April 2004, pp. 433–442 (2004)
Jiang, J., Dou, W.: A coverage-preserving density control algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In: Nikolaidis, I., Barbeau, M., Kranakis, E. (eds.) ADHOC-NOW 2004. LNCS, vol. 3158, pp. 42–55. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Sahni, S., Xu, X.: Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Networks. International Journal on Distributed Sensor Networks (2004)
Tian, D., Georganas, N.D.: A Coverage-Preserving Node Scheduling Scheme for Large Wireless Sensor Networt. In: WSNA 2002, Atlanta, Geogia, USA (September 2002)
Tian, D., Georganas, N.D.: Location and Calculation-free Node-scheduling Schemes in Large Wireless Sensor Networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2, 65–85 (2004)
Wang, X., Xing, G., Zhang, Y., Lu, C., Pless, R., Gill, C.: Integrated Coverage and Connectivity Configuration in Wireless Sensor Networks. In: ACM SenSys 2003, Los Angeles, CA, USA (November 2003)
Ye, F., Zhong, G., Lu, S., Zhang, L.: Energy Efficient Robust Sensing Coverage in Large Sensor Networks. Technical Report (2002)
Ye, F., Zhong, G., Lu, S., Zhang, L.: PEAS: A Robust Energy Conserving Protocol for Long-Lived Sensor Networks. In: ICNP 2002, Paris, France, November 2002, pp. 200–201 (2002)
Zhang, H., Hou, J.C.: Maintaining Sensing Coverage and Connectivity in Large Sensor Networks. Technical Report. UIUCDCS-R-200302351
Zhang, H., Hou, J.C.: Maintaining Coverage and Connectivity in Large Sensor Networks. The Wireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks: An International Journal (2005)
Zhang, H., Hou, J.C.: On Deriving the Upper Bound of alpha-Lifetime for Large Sensor Networks. In: MobiHoc 2004, Roppongi, Japan, May 2004, pp. 121–132 (2004)
Ganeriwal, S., Kumar, R., Srivastava, M.B.: Timing-sync protocol for sensor networks. In: ACM SenSys 2003, Los Angeles, CA, USA (November 2003)
Li, Q., Rus, D.: Global Clock Synchronization in Sensor Networks. In: Infocom 2004, Hong Kong, China (March 2004)
Savvides, A., Han, C.C., Srivastava, M.B.: Dynamic Fine-Grained Localization in Ad-Hoc Networks of Sensors. In: MobiCom 2001, Rome, Italy, July 2001, pp. 166–179 (2001)
He, T., Huang, C., Blum, B.M., Stankovic, J.A., Abdelzaher, T.: Range-Free Localization Schemes for Large Scale Sensor Networks. In: MobiCom 2003, San Diego, California, USA (September 2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bai, H., Chen, X., Ho, YC., Guan, X. (2005). Percentage Coverage Configuration in Wireless Sensor Networks. In: Pan, Y., Chen, D., Guo, M., Cao, J., Dongarra, J. (eds) Parallel and Distributed Processing and Applications. ISPA 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3758. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11576235_78
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11576235_78
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-29769-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32100-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)