Abstract
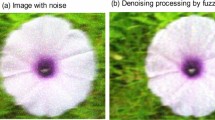
A novel segmentation algorithm for natural color image is proposed. Fibonacci Lattice-based Sampling is used to get the symbols of image so as to make each pixel’s label containing color information rather than only as a class marker. Next, Region map is formed based on Fibonacci Lattice symbols to depict homogeneous regions. On the other hand, by applying fuzzy homogeneity algorithm on the image, we filter it to acquire Edge map. To strengthen the ability of discrimination, both the weighted maps are combined to form Region-Edge map. Based on above processes, growing-merging method is used to segment the image. Finally, experiments show very promising results.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng, Y., Manjunath, B.S.: Unsupervised Segmentation of Color-Texture Regions in Image and Video. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 23, 800–810 (2001)
Kim, B.G., Park, D.J.: Unsupervised video object segmentation and tracking based on new edge features. Pattern Recognition Letter 25, 1731–1742 (2004)
Mojsilovic, A., Soljanin, E.: Color Quantization and processing by Fibonacci Lattices. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 10, 1712–1725 (2001)
Cheng, H.D., Li, J.: Fuzzy Homogeneity and Scale Space Approach to Color Image Segmentation. Pattern Recognition 36(7), 1545–1562 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Hong, Y. (2005). A Color Image Segmentation Algorithm by Using Region and Edge Information. In: Zhang, S., Jarvis, R. (eds) AI 2005: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. AI 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3809. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11589990_178
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11589990_178
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-30462-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31652-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)