Abstract
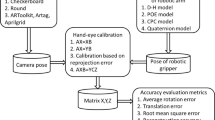
As the robot makes unplanned movement, online hand-eye calibration determines the relative pose between the robot gripper/end-effector and the sensors mounted on it. With noisy measurements, hand-eye calibration is sensitive to small rotations in real applications. Moreover, degenerate cases such as pure translations have no effect in hand-eye calibration. This paper proposes an adaptive motion selection algorithm for online hand-eye calibration, which can adaptively set the thresholds of motion selection according to the characteristics of the unplanned motion sequence. It is achieved by using polynomial-regression to predict the relationship between RMS of calibration error and thresholds. Thus, this procedure leads to an adaptive method of motion selection. It can adapt itself to online hand-eye calibration in various applications. Experiments using simulated data are conducted and present good results. Experiments using real scenes also show that the method is promising.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shiu, Y.C., Ahmad, S.: Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX = XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 5, 16–29 (1989)
Tsai, R.Y., Lenz, R.K.: A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3d robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 5, 345–358 (1989)
Chen, H.: A screw motion approach to uniqueness analysis of head-eye geometry. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Maui, Hawaii, USA, pp. 145–151 (June 1991)
Wang, C.: Extrinsic calibration of a robot sensor mounted on a robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 8(2), 161–175 (1992)
Zhuang, H., Shiu, Y.C.: A Noise-Tolerant Algorithm for Robotic Hand-Eye Calibration With or Without Sensor Orientation Measurement. IEEE Trans. on System, Man and Cybernetics 23(4), 1168–1175 (1993)
Horaud, R., Dornaika, F.: Hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Robot. Res. 14(3), 195–210 (1995)
Daniilidis, K.: Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 18(3), 286–298 (1999)
Angeles, J., Soucy, G., Ferrie, F.P.: The online solution of the hand-eye problem. IEEE Trans. Robot. Automat. 16, 720–731 (2000)
Andreff, N., Horaud, R., Espiau, B.: On-line hand-eye calibration. In: Proc. Int. Conf. on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, pp. 430–436 (October 1999)
Andreff, N., Horaud, R., Espiau, B.: Robot hand-eye calibration using structure-from-motion. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(3), 228–248 (2001)
Shi, F., Wang, J., Liu, Y.: An approach to improve online hand-eye calibration. In: Marques, J.S., Pérez de la Blanca, N., Pina, P. (eds.) IbPRIA 2005. LNCS, vol. 3522, pp. 647–655. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Regression Analysis, Numeral Statistic group, Chinese Academy of Science Beijing Science Press (1974)
Ma, S., Zhang, Z.: Computer Vision, ch. 6, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, J., Shi, F., Liu, Y. (2005). An Adaptive Selection of Motion for Online Hand-Eye Calibration. In: Zhang, S., Jarvis, R. (eds) AI 2005: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. AI 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3809. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11589990_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11589990_54
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-30462-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31652-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)