Abstract
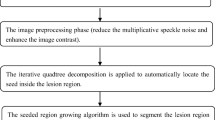
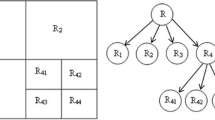
This paper proposes a rate-distortion (RD) based seeded region growing (SRG) for extracting an object such as breast tumors in ultrasound volumes which contain speckle noise and indistinct edges. In the proposed algorithm, region growing proceeds in such a way that the growing cost is minimized which is represented as the combination of rate measuring the roughness of a region contour and distortion measuring the inhomogeneity of pixels in a region. An input image is first segmented into an initial seed region and atomic homogeneous regions. The seed is next merged with one of adjacent regions which makes the RD cost minimum at each step. Such a merging is repeated until the RD cost averaged over the entire seed contour reaches the maximum. As a result, the final seed holds region homogeneity and has a smooth contour while maximizing inhomogeneity against its adjacent regions. Experiments of extracting breast tumors in four real ultrasound volumes show the proposed method yields the average 40% improvement in error rate with respect to the results extracted manually over some conventional methods.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez, R.C., Woods, R.E.: Digital Image Processing. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1993)
Martin, M., Rodriguez, E.: Energy functions for the segmentation of ultrasound volume data using active rays. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2000), vol. 4, pp. 2274–2277 (2000)
Xu, C., Prince, J.L.: Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 7, 359–369 (1998)
Ogawa, S., Itoh, K.: Three dimensional ultrasonic imaging for diagnosis of breast tumor. In: IEEE Ultrasonics Symp., pp. 1677–1680 (1998)
Krivanek, A., Sonka, M.: Ovarian ultrasound image analysis: Follicle segmentation. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging 17, 935–944 (1998)
Hao, X., Bruce, C., Pislaru, C., Greenleaf, J.: Segmenting high-frequency intracardiac ultrasound images of myocardium into infarcted, ischemic, and normal regions. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging 20, 1373–1383 (2001)
Lin, Z., Jin, J., Talbot, H.: Unseeded region growing for 3D image segmentation. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, Selected papers from the Pan-Sydney workshop on Visualization, vol. 2, pp. 31–37 (2000)
Lim, C.W., Kim, N.C., Jun, S.C., Jung, C.S.: Rate-distortion based image segmentation using recursive merging. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technology 10, 1121–1134 (2002)
Kwak, J.I., Jung, M.N., Kim, S.H., Kim, N.C.: 3D segmentation of breast tumor in ultrasound images. In: Proc. in Biomedical Optics and Imaging: Medical Imaging 2003 Ultrasonic Imaging and Signal Processing, vol. 4, pp. 193–200 (2003)
Entrekin, R., Jackson, P., Jago, J.R., Porter, B.A.: Real time spatial compound imaging in breast ultrasound: Technology and early clinical experience. Medical Mundi 43, 35–43 (1999)
Wells, P.N.T.: Absorption and dispersion of ultrasound in biological tissue. In: Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, pp. 369–376 (1975)
Xiao, G., Brady, M., Noble, A., Zhang, Y.: Segmentation of ultrasound B-Mode images with intensity inhomogeneity correction. IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging 21, 48–57 (2002)
Choi, C.S., Harashima, H., Takebe, T.: Analysis and synthesis of facial expressions in knowledge-based coding of facial image sequences. In: Proc. of ICASSP, pp. 2737–2740 (1991)
Watt, A.: Fundamental of Three-Dimensional Computer Graphics. Addison Wesley, Reading (1990)
Lango, T., Lie, T., Husby, O., Hokland, J.: Bayesian 2-D deconvolution: Effect of using spatially invariant ultrasound point spread function. IEEE Trans. on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 48 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kwak, J.I., Kim, S.H., Kim, N.C. (2005). RD-Based Seeded Region Growing for Extraction of Breast Tumor in an Ultrasound Volume. In: Hao, Y., et al. Computational Intelligence and Security. CIS 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3801. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11596448_118
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11596448_118
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-30818-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31599-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)