Abstract
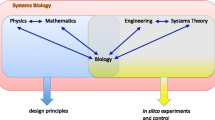
Recently, a collective effort from multiple research areas has been made to understand biological systems at the system level. On the one hand, for instance, researchers working on systems biology aim at understanding how living systems routinely perform complex tasks. On the other hand, bioscientists involved in pharmacogenomics strive to study how an individual’s genetic inheritance affects the body’s response to drugs. Among the many things, research in the above disciplines requires the ability to simulate particular biological systems as cells, organs, organisms and communities. When observed according to the perspective of system simulation, biological systems are complex ones, and consist of a set of components interacting with each other and with an external (dynamic) environment.
In this work, we propose an alternative way to specify and model complex systems based on behavioral modelling. We consider a biological system as a set of active computational components interacting in a dynamic and often unpredictable environment. Then, we propose a conceptual framework for engineering computational systems simulating the behaviour of biological systems, and modelling them in terms of agents and agent societies.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitano, H.: Foundations of Systems Biology. MIT Press, Cambridge (2002)
Finkelstein, A., Hetherington, J., Li, L., Margominski, O., Saffrey, P., Seymour, R., Warner, A.: Computational challenges of systems biology. IEEE Computer 37, 26–33 (2004)
Systems Biology Workbench, http://sbw.sourceforge.net
Systems Biology Modelling Language, http://www.sbml.org
Hucka, M., Finney, A., Sauro, H., et al.: The systems biology markup language (SBML): a medium for representation and exchange of biomedical network models. Bioinformatics 19, 524–531 (2003)
CellML, http://www.cellml.org
Bellifemine, F., Poggi, A., Rimassa, G.: Developing multi-agent systems with a fipa-compliant agent framework. Software Practice and Experience 31, 103–128 (2001)
Corradini, F., Merelli, E.: Hermes: Agent-based middleware for mobile computing. In: Bernardo, M., Bogliolo, A. (eds.) SFM-Moby 2005. LNCS, vol. 3465, pp. 234–270. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Denti, E., Omicini, A., Ricci, A.: Coordination tools for the development of agent-based systems. Applied Artificial Intelligence 16 (2002)
Cardelli, L.: Abstract machines of systems biology. In: Priami, C., Merelli, E., Gonzalez, P., Omicini, A. (eds.) Transactions on Computational Systems Biology III. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3737, pp. 145–168. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Corradini, F., Merelli, E., Vita, M.: A multi-agent system for modelling the oxidation of carbohydrate cellular process. In: Gervasi, O., Gavrilova, M.L., Kumar, V., Laganá, A., Lee, H.P., Mun, Y., Taniar, D., Tan, C.J.K. (eds.) ICCSA 2005. LNCS, vol. 3481, pp. 1265–1273. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
d’Inverno, M., Saunders, R.: Agent-based modelling of stem cell organisation in a niche. In: Brueckner, S.A., Di Marzo Serugendo, G., Karageorgos, A., Nagpal, R. (eds.) ESOA 2005. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3464, pp. 52–68. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Walker, D., Southgate, J., Hill, G., Holcombe, M., Hose, D.R., Wood, S.M., Mac Neil, S., Smallwood, R.H.: The epitheliome: agent-based modelling of the social behaviour of cells. Biosystems 76, 89–100 (2004)
Corradini, F., Mariani, L., Merelli, E.: An agent-based approach to tool integration. Journal of Software Tools Technology Transfer 6, 231–244 (2004)
Merelli, E., Young, M.: Validating MAS models with mutation. In: 1st International Workshop on Multi-Agent Systems for Medicine, Computational Biology, and Bioinformatics (MAS*BIOMED 2005), AAMAS 2005, July 25, Utrecht, The Netherlands (2005)
Kacprzak, M., Lomuscio, A., Penczek, W.: Verification of multiagent systems via unbounded model checking. In: Jennings, N.R., Sierra, C., Sonenberg, L., Tambe, M. (eds.) AAMAS 2004, vol. 2, pp. 638–645. ACM, New York (2004)
De Jong, H.: Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. Journal of Computational Biology 9, 67–103 (2002)
Antoniotti, M., Mishra, B., Piazza, C., Policriti, A., Simeoni, M.: Modeling cellular behavior with hybrid automata: Bisimulation and collapsing. In: Priami, C. (ed.) CMSB 2003. LNCS, vol. 2602, pp. 57–74. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Mendes, P.: GEPASI: a software package for modelling the dynamics, steady states and control of biochemical and other systems. Computer Applications in the Biosciences 9, 563–571 (1993)
Tomita, M., Hashimoto, K., Takahashi, K., Shimizu, T.S., Matsuzaki, Y., Miyoshi, F., Saito, K., Tanida, S., Yugi, K., Venter, J.C., Hutchison, C.A.: E-CELL: software environment for whole-cell simulation. Bioinformatics 15, 72–84 (1999)
Antoniotti, M., Policriti, A., Ugel, N., Mishra, B.: S-systems: extended s-systems and algebraic differential automata for modeling cellular behavior. In: Sahni, S.K., Prasanna, V.K., Shukla, U. (eds.) HiPC 2002. LNCS, vol. 2552, pp. 431–442. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Peleg, M., Yeh, I., Altman, R.: Modeling biological process using workflow and Petri nets. Bioinfomatics 18, 825–837 (2002)
Matsuno, H., Tanaka, Y., Aoshima, H., Doi, A., Matsui, M., Miyano, S.: Biopathways representation and simulation on hybrid functional Petri net. Silico Biology 3, 389–404 (2003)
Koch, I., Junker, B.H., Heiner, M.: Application of Petri net theory for modelling and validation of the sucrose breakdown pathway in the patato tuber. Bioinformatics 21, 1219–1226 (2005)
Nagasaki, M., Doi, A., Matsuno, H., Miyano, S.: A versatile Petri net based architecture for modeling and simulation of complex biological processes. Genome Informatics 16 (2004)
Nagasaki, M., Onami, S.: Bio-calculus: Its concept, and an application for molecular interaction. Genome Informatics 10, 133–143 (1999)
Regev, A., Silverman, W., Shapiro, E.: Representation and simulation of biochemical processes using the pi-calculus process algebra. In: Pacific Symposium of Biocomputing (PSB 2001), vol. 6, pp. 459–470 (2001)
Regev, A.: Representation and simulation of molecular pathways in the stochastic pi-calculus. In: 2nd workshop on Computation of Biochemical Pathways and Genetic Networks, Heidelberg, Germany (2001)
Chiarugi, D., Curti, M., Degano, P., Marangoni, R.: VICE: a VIrtual CEll. In: Danos, V., Schachter, V. (eds.) CMSB 2004. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3082, pp. 207–220. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Cardelli, L.: Brane calculi: Interactions of biological membranes. In: Danos, V., Schachter, V. (eds.) CMSB 2004. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3082, pp. 257–278. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Milner, R.: Communication and Concurrency. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1989)
Gonzalez, P., Cardenas, M., Camacho, D., Franyuti, A., Rosas, O., Otero, J.: Cellulat: an agent-based intracellular signalling model. BioSystems 68, 171–185 (2003)
Lazebnik, Y.: Can a biologist fix a radio?—Or, what I learned while studying apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2, 179–182 (2002)
Regev, A., Shapiro, E.: Cellular abstractions: Cells as computation. Nature 419, 343 (2002)
Zambonelli, F., Omicini, A.: Challenges and research directions in agent-oriented software engineering. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 9, 253–283 (2004)
Jennings, N.: An agent-based approach for building complex software systems. Communication of ACM 44, 35–41 (2001)
Conte, R., Edmonds, B., Moss, S., Sawyer, K.: Sociology and social theory in agent based social simulation: A symposium. Computational and Mathematical Organizational Theory 7 (2001)
Gilbert, N., Conte, R. (eds.): Artificial Societies: the computer simulation of social life. UCL Press, London (1995)
Davidsson, P.: Agent based social simulation: A computer science view. Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 5 (2002)
Parunak, V.D., Savit, R., Riolo, R.L.: Agent-based modelling vs. equation based modelling: A case study and users’ guide. In: Sichman, J.S., Conte, R., Gilbert, N. (eds.) MABS 1998. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1534, pp. 10–26. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Jennings, N., Wooldridge, M. (eds.): Agent Technololgy: Foundations, Applications, and Markets. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Wooldridge, M.J., Jennings, N.R.: Intelligent agents: Theory and practice. The Knowledge Engineering Review 10, 115–152 (1995)
Jennings, N.R.: On agent based software engineering. Artificial Intelligence 117, 277–296 (2000)
Wegner, P.: Coordination as constrained interaction. In: Hankin, C., Ciancarini, P. (eds.) COORDINATION 1996. LNCS, vol. 1061, pp. 305–320. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Ricci, A., Viroli, M., Omicini, A.: Environment-based coordination through coordination artifacts. In: Weyns, D., Van Dyke Parunak, H., Michel, F. (eds.) E4MAS 2004. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 3374, pp. 190–214. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Omicini, A., Ricci, A., Viroli, M., Castelfranchi, C., Tummolini, L.: Coordination artifacts: Environment-based coordination for intelligent agents. In: Jennings, N.R., Sierra, C., Sonenberg, L., Tambe, M. (eds.) AAMAS 2004, vol. 1, pp. 286–293. ACM, New York (2004)
KEGG: PATHWAY database, http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/pathway.html
Cliff, J., Rocha, L.M.: Towards semiotic agent-based models of socio-technical organizations. In: Sarjoughian, H., et al. (eds.) AI, Simulation and Planning in High Autonomy Systems (AIS 2000), Tucson, AZ, USA, pp. 70–79 (2000)
Richards, D., Richards, W.A., McKey, B.: Collective choices and mutual knowledge structures. Advances in Complex Systems 1, 221–236 (1998)
Omicini, A., Ossowski, S., Ricci, A.: Coordination infrastructures in the engineering of multiagent systems. In: Bergenti, F., Gleizes, M.P., Zambonelli, F. (eds.) Methodologies and Software Engineering for Agent Systems: The Agent-Oriented Software Engineering Handbook, pp. 273–296. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2004)
Sycara, K., Paolucci, M., van Velsen, M., Giampapa, J.: The RETSINA MAS infrastructure. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 7, 29–48 (2003)
Omicini, A., Zambonelli, F.: Coordination for Internet application development. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 2, 251–269 (1999) (Special Issue: Coordination Mechanisms for Web Agents)
Danos, V., Krivine, J.: Formal molecular biology. Theoretical Computer Science 325, 69–110 (2004)
Regev, A., Panina, E.M., Silverman, W., Cardelli, L., Shapiro, E.: Bioambients: An abstraction for biological compartments. Theoretical Computer Science. Special Issue on Computational Methods in Systems Biology. Elsevier 325, 141–167 (2004)
d’Inverno, M., Luck, M.: Understanding Agent Systems, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Odell, J., Parunak, H., Bauer, B.: Extending uml for agents. In: Agent-Oriented Information Systems Workshop at the 17th National conference on Artificial Intelligence (2000)
Pogson, M., Holcomb, M., Qwarnstrom, E.: An agent based model of the NF-kB signalling pathways. In: 5th International Conference on Systems Biology (ICSB 2004), Heidelberg, Germany (2004)
Garret, R., Grisham, C.: Biochemistry. Sunder College Publishing (1995)
Omicini, A., Denti, E.: From tuple spaces to tuple centres. Science of Computer Programming 41, 277–294 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cannata, N., Corradini, F., Merelli, E., Omicini, A., Ricci, A. (2005). An Agent-Oriented Conceptual Framework for Systems Biology. In: Priami, C., Merelli, E., Gonzalez, P., Omicini, A. (eds) Transactions on Computational Systems Biology III. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3737. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11599128_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11599128_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-30883-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31446-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)