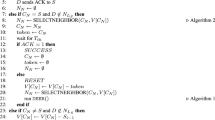Abstract
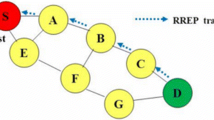
This paper presents a new routing approach for wireless networks based on the combination of both lifetime and routing cost. As the nodes in the wireless sensor and ad hoc networks are limited in power, a power failure occurs if a node has insufficient remaining energy to send a message. So, it is important to minimize the energy expenditure as well as to balance the remaining battery power among the nodes. In ad hoc networks, movement of nodes also causes frequent disconnections of routes and thus effects on network stability. Cost effective routing algorithms attempt to minimize the total power needed while lifetime prediction routing algorithms try to balance the remaining energies among the nodes in the networks. However, because of ignoring other parameter, each method fails to achieve the objective of other. The proposed routing protocol suggests a tradeoff between these two parameters, and ensures a balanced utilization to achieve maximum overall performance.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I.F., Su, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., Cayirci, E.: Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. Computer Networks 38(4), 393–422 (2002)
Chang, J.H., Tassiulas, L.: Maximum Lifetime Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 12(4), 609–619 (2004)
Huda, M.N., Hossain, M.J., Yamada, S., Kamioka, E., Chae, O.S.: Cost-Effective Lifetime Prediction Based Routing Protocol for MANET. In: Kim, C. (ed.) ICOIN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3391, pp. 170–177. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Maleki, M., Dantu, K., Pedram, M.: Lifetime Prediction Routing in Mobile Ad-Hoc Net-works. Proceedings of IEEE WCNC 2, 1185–1190 (2003)
Johnson, D.B., Maltz, D.A.: Dynamic Source Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks, pp. 153–181. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1996)
Rodoplu, V., Meng, T.H.: Minimum Energy Mobile Wireless Networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 17(8), 1333–1344 (1999)
Capkun, S., Hamdi, M., Hubaux, J.P.: GPS-Free Positioning in Mobile Ad-hoc Networks. In: Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, pp. 1–10 (2001)
Singh, S., Woo, M., Raghavendra, C.S.: Power-Aware Routing in Mobile Ad-hoc Net-works. In: Proceedings of ACM/IEEE MOBICOM, pp. 181–190 (1998)
Su, W., Lee, S.J., Gerla, M.: Mobility Prediction and Routing in Ad hoc Wireless Networks. International Journal of Network Management 11, 3–30 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hossain, M.J., Chae, O. (2005). Optimizing Lifetime and Routing Cost in Wireless Networks. In: Pal, A., Kshemkalyani, A.D., Kumar, R., Gupta, A. (eds) Distributed Computing – IWDC 2005. IWDC 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3741. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11603771_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11603771_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-30959-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32428-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)