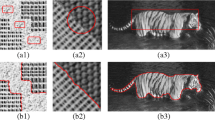
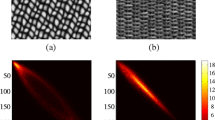
Abstract
Texture segmentation is a long standing problem in computer vision. In this paper, we propose an interactive framework for texture segmentation. Our framework has two advantages. One is that the user can define the textures to be segmented by labelling a small part of points belonging to them. The other is that the user can further improve the segmentation quality through a few interactive manipulations if necessary.
The filters used to extract the features are learned directly from the texture image to be segmented by the topographic independent component analysis. Transductive learning based on spectral graph partition is then used to infer the labels of the unlabelled points. Experiments on many texture images demonstrate that our approach can achieve good results.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuceryan, M., Jain, A.K.: Texture analysis. In: Chen, C.H., Pau, L.F., Wang, P.S.P. (eds.) The handbook of pattern recognition and computer vision, 2nd edn., pp. 207–248. World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore (1998)
Reed, T.R., du Buf, J.H.M.: A review of recent texture segmentation and feature extraction techniques. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing: Image Understanding 57, 359–372 (1993)
Joachims, T.: Transductive learning via spectral graph partitioning. In: Proc. of Int. Conf. on Machine Learning (ICML), Washington DC, USA, pp. 87–93 (2003)
Vapnik, V.N.: The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2000)
Zhu, X.J.: Semi-Supervised Learning with Graphs. PhD thesis, Carnegie Mellon University (2005)
Vapnik, V.N.: Statistical Learning Theory. John Wiley, New York (1998)
Hyvarinen, A., Hoyer, P.O., Inki, M.: Topographic independent component analysis. Neural Computation 13, 1525–1558 (2001)
Boykov, Y., Jolly, M.P.: Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary and region segmentation of objects in n-d images. In: Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver, Canada, pp. 105–112 (2001)
Rother, C., Kolmogorov, V., Blake, A.: Grabcut - interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. In: Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH, Los Angeles, USA, pp. 309–314 (2004)
Sun, J., Jia, J.Y., Tang, C.K., Shum, H.Y.: Poisson matting. In: Proc. of ACM SIGGRAPH, Los Angeles, USA, pp. 315–321 (2004)
De Bie, T., Cristianini, N.: Convex methods for transduction. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, pp. 73–80 (2003)
Blum, A., Mitchell, T.: Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. In: Proc. of Conf. on Computational Learning Theory, Amsterdam, Holand, pp. 92–100 (1998)
Joachims, T.: Transductive inference for text classification using support vector machines. In: ICML, Bled, Slovenia, pp. 200–209 (1999)
Zhang, J.G., Tan, T.N.: Brief review of invariant texture analysis methods. Pattern Recognition 35, 735–747 (2002)
Randen, T., Husoy, J.H.: Filtering for texture classification: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. On Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 21, 291–310 (1999)
Manjunath, B.S., Ma, W.Y.: Texture features for browsing and retrieval of image data. IEEE Trans. On Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 18, 837–842 (1996)
Zeng, X.Y., Chen, Y.W., Nakao, Z., Lu, H.Q.: Texture segmentation based on pattern maps obtained by independent component analysis. In: Proc. of Int. Conf. On Neural Information Processing, Shanghai, China, pp. 1189–1193 (2001)
Hyvarinen, A.: Survey on independent component analysis. Neural Computing Surveys 2, 94–128 (1999)
Yu, S.X., Shi, J.B.: Segmentation given partial grouping constraints. IEEE Trans. On Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 26, 173–183 (2004)
Bell, A.J., Sejnowski, T.J.: The independent components of natural scenes are edge filters. Vision Research 37, 3327–3338 (1997)
Brodatz, P.: Textures: A Photographics Album for Artists and Designers. Dovery, New York (1966)
MIT Vision and Modeling Group: Texture image library (1998), http://www.media.mit.edu/vismod/
Natural Image Collection for ICA Experiments: Texture image library (2001), http://www.cis.hut.fi/projects/ica/data/images/
Malik, J., Belongie, S., Shi, J.B., Leung, T.: Textons, contours and regions: Cue integration in image segmentation. In: ICCV, Corfu, Greece, pp. 918–925 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xiang, S., Nie, F., Zhang, C. (2006). Texture Image Segmentation: An Interactive Framework Based on Adaptive Features and Transductive Learning. In: Narayanan, P.J., Nayar, S.K., Shum, HY. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2006. ACCV 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3851. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11612032_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11612032_23
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-31219-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32433-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)