Abstract
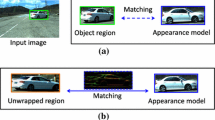
Real-time estimation of a camera’s pose relative to an object is still an open problem. The difficulty stems from the need for fast and robust detection of known objects in the scene given their 3D models, or a set of 2D images or both. This paper proposes a method that conducts a statistical analysis of the appearance of model patches from all possible viewpoints in the scene and incorporates the 3D geometry during both matching and the pose estimation processes. Thereby the appearance information from the 3D model and real images are combined with synthesized images in order to learn the variations in the multiple view feature descriptors using PCA. Furthermore, by analyzing the computed visibility distribution of each patch from different viewpoints, a reliability measure for each patch is estimated. This reliability measure is used to further constrain the classification problem. This results in a more scalable representation reducing the effect of the complexity of the 3D model on the run-time matching performance. Moreover, as required in many real-time applications this approach can yield a reliability measure for the estimated pose. Experimental results show how the pose of complex objects can be estimated efficiently from a single test image.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dementhon, D., Davis, L.S.: Model-based object pose in 25 lines of code. In: Sandini, G. (ed.) ECCV 1992. LNCS, vol. 588, Springer, Heidelberg (1992)
Pollefeys, M., Koch, R., Van Gool, L.: Self-calibration and metric reconstruction in spite of varying and unknown internal camera parameters. ICCV (1998)
Nister, D.: An efficient solution to the five-point relative pose problem. CVPR (2003)
Hartley, R., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Vacchetti, L., Lepetit, V., Fua, P.: Stable real-time 3d tracking using online and offline information. PAMI (2004)
Genc, Y., Riedel, S., Souvannavong, F., Akinlar, C., Navab, N.: Marker-less tracking for ar: A learning-based approach. ISMAR (2002)
Davison, A., Murray, D.: Simultaneous localization and map-building using active vision for a robot. PAMI (2002)
Ferrari, V., Tuytelaars, T., Van Gool, L.: Integrating multiple model views for object recognition. CVPR (2004)
Rothganger, F., Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., Ponce, J.: Segmenting, modeling, and matching video clips containing multiple moving objects. CVPR (2004)
Lowe, D.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant key points. IJCV (2004)
Meltzer, J., Soatto, S., Yang, M.H., Gupta, R.: Multiple view feature descriptors from image sequences via kernel principal component analysis. In: Pajdla, T., Matas, J(G.) (eds.) ECCV 2004. LNCS, vol. 3021, pp. 215–227. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Schmid, C., Mohr, R.: Local gray value invariants for image retrieval. PAMI (1997)
Lowe, D.G.: Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. ICCV (1999)
Van Gool, L., Moons, T., Ungureanu, D.: Affine/photometric invariants for planar intensity patters. In: Buxton, B.F., Cipolla, R. (eds.) ECCV 1996. LNCS, vol. 1065. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Mikolajczyk, K., Schmid, C.: An affine invariant interest point detector. In: Heyden, A., Sparr, G., Nielsen, M., Johansen, P. (eds.) ECCV 2002. LNCS, vol. 2350, pp. 128–142. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Schaffalitzky, F., Zisserman, A.: Multi-view matching for unordered image sets, or how do i organize my holiday snaps? In: Heyden, A., Sparr, G., Nielsen, M., Johansen, P. (eds.) ECCV 2002. LNCS, vol. 2350, pp. 414–431. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Nayar, S.K., Nene, S.A., Murase, H.: Real-time 100 object recognition system. PAMI (1996)
Li, Y., Tsin, Y., Genc, Y., Kanade, T.: Object detection using 2d spatial ordering constraints. CVPR (2005)
Lepetit, V., Pilet, J., Fua, P.: Point matching as a classification problem for fast and robust object pose estimation. CVPR (2004)
Rothganger, F., Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., Ponce, J.: 3d object modeling and recognition using affine-invariant patches and multi view spatial constraints. CVPR (2003)
Tuytelaars, T., van Gool, L.: Wide baseline stereo matching based on local, affinely invariant regions. BMVC (2000)
Allezard, N., Dhome, M., Jurie, F.: Recognition of 3d textured objects by mixing view-based and model-based representations. ICPR (2000)
Jurie, F.: Solution of the simultaneous pose and correspondence problem using gaussian error model. CVIU (1999)
Mindru, F., Moons, T., van Gool, L.: Recognizing color patterns irrespective of viewpoint and illumination. CVPR (1999)
Lepetit, V., Lager, P., Fua, P.: Randomized trees for real-time keypoint recognition. CVPR (2005)
Adelson, E.H., Bergen, J.R.: The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision. In: Computational models of visual processing, vol. 1. The MIT Press, Cambridge (1991)
Mikolajczyk, K., Tuytelaars, T., Schmid, C., Zisserman, A., Matas, J., Schaffalitzky, F., Kadir, T., Van Gool, L.: A comparison of affine region detectors. IJCV (2004)
Comaniciu, D., Meer, P.: Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. PAMI (2002)
Ke, Y., Sukthankar, R.: Pca-sift: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. CVPR (2004)
RealViz, http://www.realviz.com
Tsai, R.Y.: A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3d machine vision metrology using of the shelf tv cameras. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Najafi, H., Genc, Y., Navab, N. (2006). Fusion of 3D and Appearance Models for Fast Object Detection and Pose Estimation. In: Narayanan, P.J., Nayar, S.K., Shum, HY. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2006. ACCV 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3852. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11612704_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11612704_42
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-31244-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32432-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)