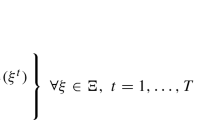Abstract
Strategic planning can be schematised as a decision making process where, given a general outline of the desirable future, the decision makers need to choose a set of actions that should coherently lead a system (corporation, institution, city, region, etc.) toward that future. A more sophisticated case is when rather than only choosing actions, the decision maker also decides the allocation of available resources among different available actions. We show that in most cases the problem can be faced using a particular Decision Network with multiple objectives, in which actions are applied simultaneously and are modelled by variables representing the efforts spent on them. The main advantage of the proposed Simultaneous Decision Network is that it can be easily built by a panel of domain experts, under the assumption of the noisy-OR causal interaction. The problem of finding the best strategy in terms of resource allocation is formulated as a combinatorial optimisation, and solved through a multi-objective meta heuristic approach.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearl, J.: Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems. Morgan Kaufman, San Mateo (1988)
Díez, F.J.: Parameter adjustment in bayes networks. the generalized noisy or-gate. In: UAI, pp. 99–105 (1993)
Zhang, W., Ji, Q.: A factorization approach to evaluating simultaneous influence diagrams. IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man and Cybernetics - A, on Systems, Man and Cybernetics - A (to appear)
Diehl, M., Haimes, Y.Y.: Influence diagrams with multiple objectives and tradeoff analysis. IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man and Cybernetics - A 34, 293–304 (2004)
Henrion, M.: Some practical issues in constructing belief networks. In: Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence 3, pp. 161–173. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (1989)
Zagorecki, A., Druzdzel, M.J.: An empirical study of probability elicitation under noisy-or assumption. In: FLAIRS Conference (2004)
de Campos, L.M., Gámez, J.A., Moral, S.: Partial abductive inference in bayesian belief networks using a genetic algorithm. Patt. Recogn. Lett. 20, 1211–1217 (1999)
Sawaragi, Y., Nakayama, H., Tanino, T.: Theory of multiobjective optimization. Academic Press, Orlando (1985)
Goldberg, D.: Genetic Algorithms and Evolution Strategy in Engineering and Computer Science: Recent Advances and Industrial Applications. Wiley, Chichester (1998)
Coello, C.C., Veldhuizen, D.V., Lamont, G.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Blecic, I., Cecchini, A., Trunfio, G.A. (2006). Simultaneous Decision Networks with Multiple Objectives as Support for Strategic Planning. In: Torra, V., Narukawa, Y., Valls, A., Domingo-Ferrer, J. (eds) Modeling Decisions for Artificial Intelligence. MDAI 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3885. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11681960_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11681960_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-32780-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-32781-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)