Abstract
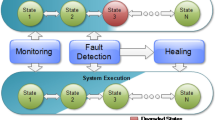
In order to construct and deploy large-scale multi-agent systems, we must address one of the fundamental issues of distributed systems, the possibility of partial failures. This means that fault-tolerance is an inevitable issue for large-scale multi-agent systems. In this paper, we discuss the issues and propose an approach for supporting fault-tolerance of multi-agent systems. The starting idea is the application of replication strategies to agents, the most critical agents being replicated to prevent failures. As criticality of agents may evolve during the course of computation and problem solving, and as resources are bounded, we need to dynamically and automatically adapt the number of replicas of agents, in order to maximize their reliability and availability. We will describe our approach and related mechanisms for evaluating the criticality of a given agent (based on application-level semantic information, e.g. interdependences, and also system-level statistical information, e.g., communication load) and for deciding what strategy to apply (e.g., active or passive replication) and how to parameterize it (e.g., number of replicas). We also will report on experiments conducted with our prototype architecture (named DimaX).
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assis-Silva, F.M., Popescu-Zeletin, R.: An approach for providing mobile agent fault tolerance. In: Rothermel, K., Hohl, F. (eds.) MA 1998. LNCS, vol. 1477, p. 14. Springer, Heidelberg (1998)
Bertier, M., Marin, O., Sens, P.: Implementation and performance evaluation of an adaptable failure detector. In: The International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, Washington, USA (2002)
Castelfranchi, C.: Dependence relations in multi-agent systems. In: Decentralized AI. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1992)
Colombetti, M., Verdicchio, M.: An analysis of agent speech acts as institutional actions. In: AAMAS-2002, pp. 1157–1164 (2002)
Fedoruk, A., Deters, R.: Improving fault-tolerance by replicating agents. In: AAMAS 2002, Bologna, Italy, pp. 373–744 (2002)
Guerraoui, R., Garbinato, B., Mazouni, K.: Lessons from designing and implementing GARF. In: Object-Based Parallel and Distributed Computation 1993. LNCS, vol. 791, pp. 238–256. Springer, Heidelberg (1995)
Guessoum, Z., Briot, J.-P.: From active objects to autonomous agents. IEEE Concurrency 7(3), 68–76 (1999)
Guessoum, Z., Briot, J.-P., Marin, O., Hamel, A., Sens, P.: Dynamic and adaptive replication for large-scale reliable multi-agent systems. In: Garcia, A.F., de Lucena, C.J.P., Zambonelli, F., Omicini, A., Castro, J. (eds.) Software Engineering for Large-Scale Multi-Agent Systems. LNCS, vol. 2603, pp. 182–198. Springer, Heidelberg (2003)
Guessoum, Z., Faci, N., Briot, J.-P.: Adaptive replication of large-scale multiagent systems - towards a fault-tolerant multi-agent platform. In: Proceedings of the ICSE 2005 Fourth International Workshop on Software Engineering for Large-Scale Multi-Agent Systems (SELMAS 2005). ACM, New York (2006)
Hagg, S.: A sentinel approach to fault handling in multi-agent systems. In: Dickson, L., Zhang, C. (eds.) DAI 1996. LNCS, vol. 1286, pp. 190–195. Springer, Heidelberg (1997)
Horling, B., Benyo, B., Lesser, V.: Using self-diagnosis to adapt organizational structures. In: 5th International Conference on Autonomous Agents, Montreal, pp. 529–536. ACM Press, New York (2001)
Kaminka, G.A., Pynadath, D.V., Tambe, M.: Monitoring teams by overhearing: A multi-agent plan-recognition approach. Journal of Intelligence Artificial Research 17, 83–135 (2002)
Kraus, S., Subrahmanian, V.S., Cihan Tacs, N.: Probabilistically survivable MASs. In: IJCAI 2003, pp. 789–795 (2003)
Malone, T.W., Crowston, K.: The interdisciplanary study of coordination. ACM Computing Surveys 26(1), 87–119 (1994)
Marin, O., Bertier, M., Sens, P.: DARX - a framework for the fault-tolerant support of agent software. In: 14th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE 2003), Denver, Colorado, USA, pp. 406–417. IEEE, Los Alamitos (2003)
Klein, M., Rodriguez-Aguilar, J.A., Dellarocas, C.: Using domain-independent exception handling services to enable robust open multi-agent systems: The case of agent death. Journal of autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 7(1-2), 179–189 (2003)
OMG TC Document ormsc/2001 07-01. Model driven architecture (mda). Technical report, OMG (2001)
Van Renesse, R., Birman, K., Maffeis, S.: Horus: A flexible group communication system. Communications of the ACM 39(4), 76–83 (1996)
Roos, N., Teije, A.t., Witteveen, C.: A protocol for multi-agent diagnosis with spatially distributed knowledge. In: First Workshop on Programming Multiagent Systems: Languages, frameworks, techniques, and tools (ProMAS 2003), AAMAS 2003, pp. 655–661. ACM, New York (2003)
Sichman, J.S., Conte, R.: Multi-agent dependence by dependence graphs. In: AAMAS 2002, Bologna, Italy, pp. 483–490. ACM, New York (2002)
Sichman, J.S., Conte, R., Demazeau, Y.: Reasoning about others using dependence networks. In: Actes de Incontro del gruppo AI*IA di interesse speciale sul inteligenza artificiale distribuita, Roma, Italia (1993)
Sichman, J.S., Conte, R., Demazeau, Y.: A social reasoning mechanism based on dependence networks. In: Proceedings of ECAI 1994 - European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (August 1994)
Silva, L., Batista, V., Silva, J.: Fault-tolerant execution of mobile agents. In: International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, pp. 135–143 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guessoum, Z., Faci, N., Briot, JP. (2006). Adaptive Replication of Large-Scale Multi-agent Systems – Towards a Fault-Tolerant Multi-agent Platform. In: Garcia, A., Choren, R., Lucena, C., Giorgini, P., Holvoet, T., Romanovsky, A. (eds) Software Engineering for Multi-Agent Systems IV. SELMAS 2005. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3914. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11738817_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11738817_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-33580-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-33583-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)