Abstract
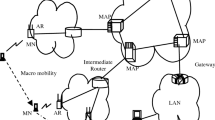
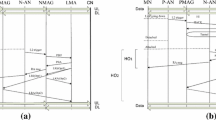
MIPv6 provides the L3 connectivity when the IPv6 mobile node moves between subnets. Nevertheless, the mobile node cannot receive IP packet because of the handover latency. The handover latency is not efficient to provide the real-time multimedia application service. Notable protocols of the extensions of MIPv6 are FMIPv6 and HMIPv6. In HMIPv6, if the mobile node moves from one access router to another in the different MAP domain, such a movement is called macro mobility handover, then the mobile node creates a new RCoA and LCoA and performs registration with the new MAP and HA. Until the address registration with MAP and HA complete, the mobile node cannot receive IP packet. Therefore, we need to execute the macro mobility handover efficiently and reduce the handover latency and packet loss. We propose a method to perform the macro mobility handover efficiently in HMIPv6. To provide seamless service and minimize packet loss when the mobile node performs the macro mobility handover, we will adjust the fast handover technology of FMIPv6 to the MAP’s characteristics in the proposed scheme. To reduce the handover latency and packet loss, we use a tunnel between the edge access routers and perform the L3 handover earlier before the L2 handover. We compare the procedure of the macro mobility handover of the proposed scheme with the original HMIPv6 by means of using the cost analysis comparison. We observe that the proposed scheme can be reduced the 82% of the total cost of the macro mobility handover of the original HMIPv6.
This work was supported by grant No. (R01-2004-000-10618-0) from the Basic Research Program of the Korea Science & Engineering Foundation.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson, D., Perkins, C., Arkko, J.: Mobility Support in IPv6, RFC 3775, IETF (2004)
Koodli, R., et al.: Fast Handovers for Mobile IPv6, RFC 4068, IETF (2005)
Soliman, H., Castelluccia, C., El Malki, K., Bellier, L.: Hierarchical MIPv6 Mobility Management (HMIPv6), RFC 4140, IETF (2005)
Droms, R., Bound, J., Volz, B., Lemon, T., Perkins, C., Carney, M.: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6), RFC 3315, IETF (2003)
Thomson, S., Narten, T.: IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration, RFC 2462, IETF (1998)
Narten, T., Nordmark, E., Simpson, W.: Negihbor Discovery for IP version 6 (IPv6), RFC 2461, IETF (1998)
Jain, R., Raleigh, T., Graff, C., Bereschinsky, M.: Mobile Internet Access and QoS Quarantees using Mobile IP and RSVP with Location Registers. In: Proc. ICC 1998 Conf. (1998)
Pack, S., Choi, Y.: Performance Analysis of Fast Handover in Mobile IPv6 Networks. In: Proc. IFIP PWC 2003, Venice, Italy (2003)
Kim, J., Mun, Y.: A study on Handoff Performance Improvement Scheme for Mobile IPv6 over IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN, Master Thesis, Soongsil University (2003)
Vatn, J.: An experimental study of IEEE 802.11b handover performance and its effect on voice traffic, SE telecommunication Systems Laboratory Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, IMIT (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lee, K., Lim, Y., Ahn, S., Mun, Y. (2006). A Macro Mobility Handover Performance Improvement Scheme for HMIPv6. In: Gavrilova, M.L., et al. Computational Science and Its Applications - ICCSA 2006. ICCSA 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3981. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11751588_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11751588_43
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34072-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34074-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)