Abstract
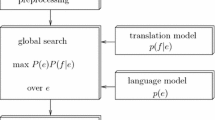
The innovative feature of the system presented in this paper is the use of pattern-matching techniques to retrieve translations resulting in a flexible, language-independent approach, which employs a limited amount of explicit a priori linguistic knowledge. Furthermore, while all state-of-the-art corpus-based approaches to Machine Translation (MT) rely on bitexts, this system relies on extensive target language monolingual corpora. The translation process distinguishes three phases: 1) pre-processing with ‘light’ rule and statisticsbased NLP techniques 2) search & retrieval, 3) synthesising. At Phase 1, the source language sentence is mapped onto a lemma-to-lemma translated string. This string then forms the input to the search algorithm, which retrieves similar sentences from the corpus (Phase 2). This retrieval process is performed iteratively at increasing levels of detail, until the best match is detected. The best retrieved sentence is sent to the synthesising algorithm (Phase 3), which handles phenomena such as agreement.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Onaizan, Y., Germann, U., Hermjakob, U., Knight, K., Koehn, P., Marcu, D., Yamada, K.: Translating with Scarce Resources. In: American Association for Artificial Intelligence conference (AAAI 2000), Austin, Texas, pp. 672–678 (2000), available at http://www.isi.edu/natural-language/projects/rewrite
Boutsis, S., Prokopidis, P., Giouli, V., Piperidis, S.: A Robust Parser for Unrestricted Greek Text. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Athens, Greece, vol. 1, pp. 467–482 (2000)
Brown, P., Cocke, J., Della Pietra, S., Della Pietra, V., Jelinek, F., Lafferty, J., Mercer, R., Roosin, P.S.: A Statistical Approach to Machine Translation. Computational Linguistics 16(2), 79–85 (1990)
Cranias, L., Papageorgiou, H., Piperidis, S.: Example Retrieval from a Translation Memory. Natural Language Engineering 3, 255–277 (1997)
Dologlou, I., Markantonatou, S., Tambouratzis, G., Yannoutsou, O., Fourla, A., Ioannou, N.: Using Monolingual Corpora for Statistical Machine Translation. In: Proceedings of EAMT/CLAW 2003, Dublin, Ireland, pp. 61–68 (2003)
Ioannou, N.: METIS: Statistical Machine Translation Using Monolingual Corpora. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Text Processing for Modern Greek: From Symbolic to Statistical Approaches (held in conjunction with the 6th International Conference of Greek Linguistics), Rethymno, Greece, pp. 11–21 (2003)
Labropoulou, P., Mantzari, E., Gavrilidou, M.: Lexicon-Morphosyntactic Specifications: Language Specific Instantiation (Greek), PP-PAROLE, MLAP report, pp. 63–386 (1996)
McTait, K.: Translation Patterns, Linguistic Knowledge and Complexity in EBMT. In: Carl, M., Way, A. (eds.) Recent Advances in Example-Based Machine Translation, pp. 307–338. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2003)
Nagao, M.: A Framework of a Mechanical Translation between Japanese and English by Analogy Principle. In: Elithorn, A., Banerji, R. (eds.) Artificial and Human Intelligence, North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Nist: Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation Quality Using n-gram Co-occurrences Statistics (2002); available at http://www.nist.gov/speech/tests/mt/
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., Zhu, W.-J.: BLEU: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, USA, pp. 311–318 (2002)
Popovic, M., Ney, H.: Exploiting Phrasal Lexica and Additional Morpho-Syntactic Language Resources for Statistical Machine Translation with Scarce Training Data. In: EAMT 10th Annual Conference, Budapest, Hungary (2005)
Vandeghinste, V.: Manual for ShaRPa 2.0. Internal Report, Centre for Computational Linguistics, K.U.Leuven (2005)
Way, A.: Translating with Examples: The LFG-DOT Models of Translation. In: Carl, M., Way, A. (eds.) Recent Advances in Example-Based Machine Translation, pp. 443–472. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tambouratzis, G., Sofianopoulos, S., Spilioti, V., Vassiliou, M., Yannoutsou, O., Markantonatou, S. (2006). Pattern Matching-Based System for Machine Translation (MT). In: Antoniou, G., Potamias, G., Spyropoulos, C., Plexousakis, D. (eds) Advances in Artificial Intelligence. SETN 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3955. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11752912_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11752912_35
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34117-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34118-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)