Abstract
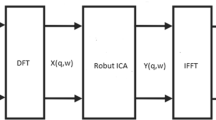
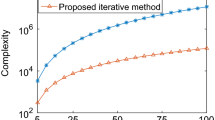
In this paper, a convolutive blind source separation (BSS) algorithm based on a double-iteration method is proposed to process the convolutive mixed non-white broadband signals. By sliding Fourier transform (SFT), the convolutive mixture problem is changed into instantaneous case in time-frequent domain, which can be solved by applying an instantaneous separation method for every frequent bin. A novel cost function for each frequent bin based on joint diagonalization of a set of correlation matrices with multiple time-lags is constructed. Through combination of the proposed double-iteration method with a restriction on the length of inverse filter in time domain, the inverse of transfer channel or separation matrix, which has consistent permutations for all frequencies, can be estimated. Then it is easy to calculate the recovered source signals. The results of simulations also illustrate the algorithm has not only fast convergence performance, but also higher recovered accuracy and output SER (Signal to Error of reconstruction Ratio).
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comon, P.: Blind Separation of Source: A New Concept. Signal Processing 36(3), 287–314 (1994)
Cardoso., J.F.: Blind Signal Separation Statistics Principles. Proc. of. IEEE 86(10), 2009–2025 (1998)
Futoshi, A., Shiro, I.: Michiaki. O. Hideki. A., Nobuhiko. K.: A Combined Approach if Array Processing and Independent Component Analysis for Blind Separation of Acoustic Signals. 0-703-7042. IEEE (2001)
Belouchrani, A., Moeness, G.: Amin: Blind Source Separation Based on Time-Frequency Signal Representations. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing 46(11), 2888–2897 (1998)
Peterson, M.: Simulating the Response of Multiple Microphones to a Single Acoustic Source in a Reverberant Room. J. Acoustic. Soc. Amer. 80(11), 1527–1529 (1986)
Parra, L., Spence, C.: Convolutive Blind Separation of Non-Stationary Source. IEEE Transaction on Speech and Audio Processing 8(5), 320–327 (2000)
Bucher., H., Aichner, R., Kellermann, W.: A Generalization of Blind Source Separation Algorithms for Convolutive Mixtures Based on Second-Order Statistics. IEEE Transaction on Speech an Audio Processing 13(1), 120–134 (2005)
Asano, F., Hayamizu, S., Yamada, T., Nakamura, S.: Speech Enhancement Based on the Subspace Method. IEEE Transaction on SAP 8(9), 497–507 (2000)
Hopfied, J.J.: Neural Networks and Physical System with Emergent Collective Computational Abilities. Proc. Natl, Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2554–2558 (1982)
LaSalle, J.P.: The Stability of Dynamical Systems. SIAM Press, Philadelphia (1976)
Dapena, A., Serviere, C., Castedo, L.: Inversion of the Sliding Fourier Transform Using Only Two Frequency Bins and Its Application to Source Separation. Signal Processing 83, 453–457 (2003)
Feng, D.Z., Zhang, X.D., Bao, Z.: An Efficient Multistage Decomposition Approach for Independent Components. Signal Processing 83(1), 181–197 (2003)
All the data and mixed filter in this paper can be obtained on http://-www2.elc.tur.nl//ica99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, H., Feng, D. (2006). Convolutive Blind Separation of Non-white Broadband Signals Based on a Double-Iteration Method. In: Wang, J., Yi, Z., Zurada, J.M., Lu, BL., Yin, H. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks - ISNN 2006. ISNN 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3971. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11759966_177
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11759966_177
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34439-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34440-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)