Abstract
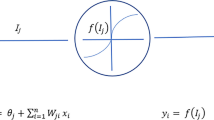
With the accumulating of the strong earthquakes records, it becomes practicable to achieve the more accurate attenuation relationships. Based on the seismic records of West American, the Radial Basis Function (RBF) and Back Propagation (BP) artificial neural networks model are respectively constructed for three-dimensional seismic parameters attenuation relationship. The RBF model is nice fitting for the training data, although it has great errors on other tested points. While the BP model is not good than the RBF model for the training data, it possesses a better consecutive property in the whole area. It is a proper neural network model for the problem. After training with the selected records, the Neural Networks (NN) shows a good fitting with the training records. And it is easy to construct three-dimensional model to predict the attenuation relationship. In order to demonstrate the efficiency of the presented methodology, the contrast is discussed for the results of the BP model and three typical traditional attenuation formulae.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhen, G.F., Tao, X.X.: Construct the Intensity Attenuation Relation Using ANN Method. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration 13(1), 60–66 (1993)
Wang, H.S.: Intelligent Prediction of the Peak Seismic Parameters Based On ANN. Journal of Seismology 15(2), 208–216 (1993)
Cui, J.W., Fan, Y.X., Wen, R.Z.: Establishment of Attenuation Law of Acceleration Peak Value by Using Neural Network. Earthquake Research 20(3), 296–306 (1997)
Joyner, W.B., Boore, D.M.: Peak Attenuation and Velocity from Strong-Motion Records Including Records from 1979 Imperial Valley, California, Earthquake. Bulletin of Seismology Society of America 71(6), 2011–2038 (1981)
Huo, J.R.: Near Field Ground Motion Attenuation Research. Ph. D. Thesis of the Institute Of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration (1989)
Wang, G.X., Tao, X.X.: A New Two-Steps Method for Fitting Ground Motion Attenuation Relationship. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration 20(1), 25–28 (2000)
Boore, D.M., Joyner, W.B., Fumal, T.E.: Estimation of Response Spectra and Peak Accelerations from North America Earthquakes: an Interim Report. U. S. Geol. Surv. Open File Report, 93–509 (1993)
Boore, D.M., Joyner, W.B., Fumal, T.E.: Estimation of Response Spectra and Peak Accelerations from North America Earthquakes: Part 2, Interim Report. U. S. Geol. Surv. Open File Report, 94–127 (1994)
Hu, Y.X., Zhang, Y.M., Shi, Z.L.: Training Material for the Code of Evaluation of Seismic Safety for Engineering Sites. Engineering Earthquake Research Center (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, By., Ye, Ly., Xiao, Ml., Miao, S., Su, Jy. (2006). Artificial Neural Network Methodology for Three-Dimensional Seismic Parameters Attenuation Analysis. In: Wang, J., Yi, Z., Zurada, J.M., Lu, BL., Yin, H. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks - ISNN 2006. ISNN 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3973. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11760191_178
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11760191_178
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34482-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34483-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)