Abstract
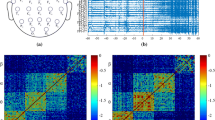
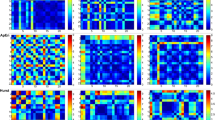
EEG recordings are widely used in epilepsy research. We intend to address a question whether small world network property exists in neural networks when epileptic seizures occur. In this paper, we introduce a bispectrum analysis to calculate the interaction between two EEG recordings; then, a suitable threshold is chosen to convert the interaction of the six channels at five frequency bands to a sparse graph (node: n=30, edge: k=4-7). Through analyzing a real EEG recording, it is found the clustering coefficient is similar to that of regular graph; however the path length is less than that of regular graph. Thus a primary suggestion can be made that neural networks possess small world network characteristic. During epileptic seizures, the small world property of neural network is more significant.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iasemidis, L.D., Pardalos, P.M., Principe, J.C.: Adaptive Epileptic Seizure Prediction System. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 50, 616–627 (2003)
Hoeve, M.J., Jones, R.D., Carroll, G.J., Goelz, H.: Automated Detection of Epileptic Seizures in the EEG. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Istanbul, Turkey, vol. 3, pp. 943–946 (2001)
Albert, R., Barabasi, A.L.: Statistical Mechanics of Complex Networks. Review of Modern Physics 74, 47–97 (2002)
Albert, R., Barabasi, A.L.: Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks. Science 286, 509–512 (1999)
Pikovsky, A.S., Rosenblum, M., Kurths, J.: Synchronization, a Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Pikovsky, A.S., Rosenblum, M.G., Osipov, G.V., Kurths, J.: Phase Synchronization of Chaotic Oscillators by External Driving. Physica D 104, 219–238 (1997)
Helme, B.I., Nikias, C.L.: Improved Spectrum Performance via a Data Adaptive Weighted Burg Technique. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 33, 903–910 (1985)
Nikias, C.L., Raghuveer, M.R.: Multidimensional Parametric Spectral Estimation. Signal Processing 9, 280–290 (1985)
Shen, C., Lemmin, U.: Ultasonic Intensity Power Spectrum Estimation by Using the Bispectral Reconstrucion Technique. Signal Processing 61, 39–44 (1997)
Sigl, J.C., Chamoun, N.G.: An Introduction of Bispectral Analysis for the Electroencephalogram. Journal of Clinical Monitoring 10, 392–404 (1994)
Hinich, M.J., Clay, C.S.: The Application of the Discrete Fourier Transform in the Estimation of Power Spectra, Coherence and Bispectra of Geophysical Data. Review of Geophysics 6, 347–363 (1968)
Swami, A., Mendel, J.M., Nikias, C.L. (Max): Higher-Order Spectral Analysis Toolbox. The MathWorks, Inc. (1998)
Kochen, M. (ed.): The Small World., Ablex, Norwood, New Jersey (1989)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective Dynamics of ‘Small-World’ Networks. Nature 393, 440–442 (1998)
Olaf, S., Jonathan, D.Z.: The Small World of the Cerebral Cortex. Neuroinformatics 2, 145–162 (2004)
Maiwald, T., Winterhalder, M., Aschenbrenner-Scheibe, R., Voss, H.U., Schulze-Bonhage, A., Timmera, J.: Comparison of Three Nonlinear Seizure Prediction Methods by Means of the Seizure Prediction Characteristic. Physica D 194, 357–368 (2004)
Aschenbrenner-Scheibe, R., Maiwald, T., Winterhalder, M., Voss, H.U., Timmer, J., Schulze-Bonhage, A.: How Well Can Epileptic Seizures Be Predicted? An Evaluation of a Nonlinear Method. Brain 126, 2616–2626 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, H., Li, X., Guan, X. (2006). Networking Property During Epileptic Seizure with Multi-channel EEG Recordings. In: Wang, J., Yi, Z., Zurada, J.M., Lu, BL., Yin, H. (eds) Advances in Neural Networks - ISNN 2006. ISNN 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3973. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11760191_84
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11760191_84
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34482-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34483-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)