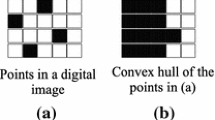
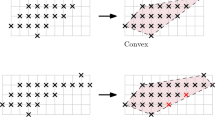
Abstract
Polygonal representations of digital sets with the same convexity properties allow a simple decomposition of digital boundaries into convex and concave parts.
Representations whose vertices are boundary points, i.e. are integer numbers, attract most attention. The existing linear Algorithm UpPolRep computes polygonal representations with some uncorresponding parts. However, the algorithm is unable to decide if a corresponding polygonal representation still exists and in the case of existence it is unable to compute the representation. Studying situations where uncorrespondences appear we extended the algorithm. The extention does not change the time complexity. If a digital set possesses a corresponding representation then it detects this representation. Otherwise, it recognizes that such representation does not exist.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debled-Rennesson, I., Reveillès, J.-P.: A linear algorithm for segmentation of digital curves. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 9, 635–662 (1995)
Debled-Rennesson, I., Rémy, J.-L., Rouyer-Degli, J.: Detection of discrete convexity of polyominoes. Discrete Applied Mathematics 125, 115–133 (2003)
Dörksen, H.: Shape Representations of Digital Sets based on Convexity Properties. Dissertation. Fachbereich Mathematik. Universität Hamburg (2004), http://www.sub.uni-hamburg.de/opus/volltexte/2005/2332/
Dörksen-Reiter, H., Debled-Rennesson, I.: Convex and Concave Parts of Digital Curves. In: Klette, R., et al. (eds.) Geometric Properties from Incomplete Data, Computational Imaging and Vision, vol. 31. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Eckhardt, U., Reiter, H.: Polygonal Representations of Digital Sets. Algorithmica 38(1), 5–23 (2004)
Feschet, F., Tougne, L.: Optimal time computation of the tangent of a discrete curve: application to the curvature. In: Bertrand, G., Couprie, M., Perroton, L. (eds.) DGCI 1999. LNCS, vol. 1568, pp. 31–40. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Freeman, H.: On the encoding of arbitrary geometry configurations. IRE Trans. EC 10, 260–268 (1961)
Klette, R., Rosenfeld, R.: Digital Geometry. Morgan Kaufmann publishers, Elsevier (2004)
Hübler, A.: Diskrete Geometrie für die Digitale Bildverarbeitung. Dissertation B. Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena (1989)
Latecki, L., Lakämper, R.: Convexity rule for shape decomposition based on discrete contour evolution. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 73(3), 441–454 (1999)
Reveillès, J.-P.: Géométrie discrète, calcul en nombres entiers et algorithmique. Thése d’État, Strasbourg (1991)
Scherl, W.: Bildanalyse allgemeiner Dokumente. (Informatik-Fachberichte, Band 131). Springer, Heidelberg (1987)
Valentine, F.A.: Convex Sets. McGraw-Hill Series in Higher Mathematics. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York (1964)
Voss, K.: Discrete Images, Objects and Functions in ℤn. Algorithm and Combinatorics, vol. 11. Springer, Heidelberg (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dörksen-Reiter, H., Debled-Rennesson, I. (2006). A Linear Algorithm for Polygonal Representations of Digital Sets. In: Reulke, R., Eckardt, U., Flach, B., Knauer, U., Polthier, K. (eds) Combinatorial Image Analysis. IWCIA 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4040. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11774938_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11774938_24
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-35153-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-35154-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)