Abstract
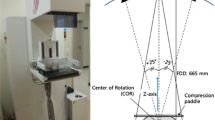
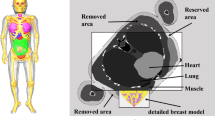
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a tomographic technique in which individual slices through the breast are reconstructed from x-ray projection images acquired over a limited angular range. In contrast-enhanced DBT (CE-DBT) functional information is observed by administration of an radiographic contrast agent. The uptake of iodine in the breast is very small and causes changes in x-ray transmission that are smaller than 5%. This presents significant technical challenges if quantitative assessment of contrast agent concentration in tissue is desired. We modeled CE-DBT acquisition by simulating x-ray spectra from 40 to 49 kV. Comparison of attenuation data of our simulated and measured spectra were found to agree well. We investigated the effect of patient motion and scatter on iodine uptake. These parameters were evaluated by means of experiments and theoretical modeling.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carton, A.-K., Li, J., Albert, M., et al.: Quantification for contrast-enhanced digital breast tomosynthesis. In: Flynn, M.J., Hsieh, J. (eds.) Medical Imaging 2006: Physics of Medical Imaging, pp. 111–121 (2006)
Jong, R.A., Yaffe, M.J., Skarpathiotakis, M., et al.: Contrast-enhanced digital mammography: Initial clinical experience. Radiology 228, 842–850 (2003)
Skarpathiotakis, M., Yaffe, M.J., Bloomquist, A.K., et al.: Development of contrast digital mammography. Medical Physics 29(10), 2419–2426 (2002)
Maidment, A.D.A., Adelow, L., Blom, O., et al.: Evaluation of a Photon-Counting Breast Tomosynthesis Imaging System. In: Flynn, M.J. (ed.) Physics of Medical Imaging, Proc. SPIE, vol. 6142 (2006)
Wu, T., Moore, R.H., Rafferty, E.A., et al.: Breast tomosynthesis: Methods and applications. In: Karellas, A. (ed.) RSNA Categorical Course in Diagnostic Radiology Physics: Advances in Breast Imaging - Physics, Technology, and Clinical Applications, pp. 149–163 (2004)
Dobbins III, J.T., Godfrey, D.J.: Digital x-ray tomosynthesis: current state of the art and clinical potential. Physics in Medicine & Biology 48(19), 65–106 (2003)
Niklason, L.T., Christian, B.T., Niklason, L.E., et al.: Digital tomosynthesis in breast imaging. Radiology 205(2), 399–406 (1997)
Boone, J.M., Fewell, T.R., Jennings, R.J.: Molybdenum, rhodium, and tungsten anode spectral models using interpolating polynomials with application to mammography. Medical Physics 24(12), 1863–1874 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Carton, AK., Li, J., Chen, S., Conant, E., Maidment, A.D.A. (2006). Optimization of Contrast-Enhanced Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. In: Astley, S.M., Brady, M., Rose, C., Zwiggelaar, R. (eds) Digital Mammography. IWDM 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4046. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11783237_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11783237_26
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-35625-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-35627-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)