Abstract
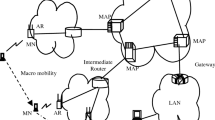
Mobile IPv6 represents a global solution, providing mobility management for a wide variety of radio technologies, devices, and applications. In particular, Network Mobility basic support protocol is the one of fundamental solutions in MIPv6 which reduces the number of binding update messages issued from mobile network nodes except mobile routers. That is, it never reduces the number of binding update messages which mobile router issues. Significant research results relating to Network Mobility have been reported over last several years. However, practical and common issues exist within the technology; specification of Binding Update Lifetime has a substantial impact the system performance. The binding update message should be delivered periodically for the purpose of user location notification and binding authorization. If the lifetime is too short, the traffic load resulting from the messages may be significant. In addition, issues related to authorization can be problematic. In this paper, therefore, Network Mobility considering arrival time is devised to solve the binding update explosion of mobile routers without security problem in Network Mobility.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perkins, C.: IP mobility support for IPv4, RFC 3344 (August 2002)
Johnson, B., Perkins, C., Arkko, J.: Mobility Support in IPv6, RFC 3775 (June 2004)
Devarapalli, V., Wakikawa, R., Petrescu, A., Thubert, P.: Network Mobility (NEMO) Basic Support Protocol, RFC 3963, IETF (January 2005)
Inoue, T., Takahashi, N., Miyazaki, T.: Hierarchical Location Management Scheme Based on Collaboration of Mobile Nodes. IEICE Trans. Commn. E87-B(3), 470–479 (2004)
Arkko, J., Vogt, C.: Credit-Based Authorization for Binding Lifetime Extension, draft-arkko-mipv6-binding-lifetime-extension-00 (2004)
Ng, C., Hirano, J.: Extending Return Routability Procedure for Network Prefix (RRNP), Internet Draft, draft-ng-nemo-rrnp-00.txt (October 2004)
Lin, Y.B., Lai, W.R., Chen, R.J.: Performance Analysis for Dual Band PCS Networks. IEEE Journal on Trans. on Computers 49(2), 148–159 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, S.O., Kim, S. (2006). Network Mobility in MIPv6 Considering Arrival Time. In: Sha, E., Han, SK., Xu, CZ., Kim, MH., Yang, L.T., Xiao, B. (eds) Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing. EUC 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4096. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11802167_62
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11802167_62
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-36679-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36681-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)