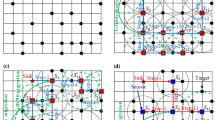
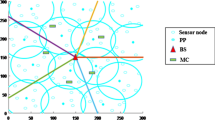
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a relay shift based approach to solve uneven sensor distribution problem due to the initial random dropping or the existence of faulty sensors. The distinguishing feature of our work is that the sensors in our model have limited mobility. After determining the optimal cluster head positions by particle swarm optimization (PSO) method, we use proposed Relay Shift Based Algorithm (RSBA) for movement assisted sensor deployment. Dijkstra’s algorithm is applied to find a shortest path from a redundant sensor to a virtual node point in an uncovered area, and each sensor moves along this path by relay shift based on the principle that evenly distributed sensors can provide better coverage. Simulation results show that our approach can provide high coverage within a short time and limited movement distance as well as ensuring connectivity and energy efficiency.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meguerdichian, S., Koushanfar, F., Qu, G., Potkonjak, M.: Exposure in Wireless Ad-Hoc Sensor Networks. In: Mobicom (2001)
Dhillon, S., Chakrabarty, K., Iyengar, S.: Sensor placement for grid coverage under imprecise detections. In: Proc. International Conference on Information Fusion (2002)
Clouqueur, T., Phipatanasuphorn, V., Ramanathan, P., Saluja, K.k.: Sensor Deployment Strategy for Target Detection. In: WSNA (2002)
Tilak, S., AbuGhazaleh, N.B., Heinzelman, W.: Infrastructure Tradeoffs for Sensor Networks. In: WSNA (2002)
Howard, A., Mataric, M.J., Sukhatme, G.S.: An Incremental Self-Deployment Algorithm for Mobile Sensor Networks. Autonomous Robots, Special Issue on Intelligent Embedded Systems (September 2002)
Wu, J., Wang, S.: Smart: A scan-based movement-assisted deployment method in wireless sensor networks. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM Conference, Miami (March 2005)
Wang, G., Cao, G., La Porta, T.: Movement-assisted sensor deployment. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM Conference, Hong Kong (2004)
Zou, Y., Chakrabarty, K.: Sensor deployment and target localization based on virtual forces. In: Proc. IEEE INFOCOM Conference, vol. 2, pp. 1293–1303 (2003)
Heo, N., Varshney, P.K.: Energy-Efficient Deployment of Intelligent Mobile Sensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics—Part A: Systems And Humans 35(1), 78–92 (2005)
Wu, X., Lei, S., Jie, Y., Hui, X., Cho, J., Lee, S.: Swarm Based Sensor Deployment Optimization in Ad hoc Sensor Networks. In: Yang, L.T., Zhou, X.-s., Zhao, W., Wu, Z., Zhu, Y., Lin, M. (eds.) ICESS 2005. LNCS, vol. 3820, pp. 533–541. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Chellappan, S., Bai, X., Ma, B., Xuan, D.: Mobility Limited Flip-based Sensor Networks Deployment. Dept. of Computer Science and Eng., Ohio-State Univ. Technique report (2005)
Chellappan, S., Bai, X., Ma, B., Xuan, D.: Sensor Networks Deployment Using Flip-based Sensors. In: Proc. of IEEE International Conference MASS 2005 (2005)
Stoleru, R., He, T., Stankovic, J.A., Luebke, D.: A High-Accuracy, Low-Cost Localization System for Wireless Sensor Networks. In: ACM conference Sensys (2005)
Heinzelman, W.B., Chandrakasan, A.P., Balakrishnan, H.: An Application-Specific Protocol Architecture for Wireless Microsensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 1(4), 660–670 (2002)
Cormen, T.H., Leiserson, C.E., Rivest, R.L., Stein, C.: Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd edn., pp. 595–601. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, X., Niu, Y., Shu, L., Cho, J., Lee, Y., Lee, S. (2006). Relay Shift Based Self-deployment for Mobility Limited Sensor Networks. In: Ma, J., Jin, H., Yang, L.T., Tsai, J.JP. (eds) Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing. UIC 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4159. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11833529_57
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11833529_57
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-38091-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-38092-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)