Abstract
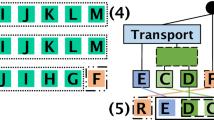
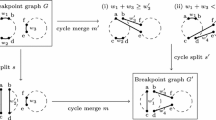
Preliminary to most comparative genomics studies is the annotation of chromosomes as ordered sequences of genes. Unfortunately, different genetic mapping techniques usually give rise to different maps with unequal gene content, and often containing sets of unordered neighboring genes. Only partial orders can thus be obtained from combining such maps. However, once a total order O is known for a given genome, it can be used as a reference to order genes of a closely related species characterized by a partial order P. In this paper, the problem is to find a linearization of P that is as close as possible to O in term of the breakpoint distance. We first prove an NP-complete complexity result for this problem. We then give a dynamic programming algorithm whose running time is exponential for general partial orders, but polynomial when the partial order is derived from a bounded number of genetic maps. A time-efficient greedy heuristic is then given for the general case, with a performance higher than 90% on simulated data. Applications to the analysis of grass genomes are presented.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bérard, S., Bergeron, A., Chauve, C.: Conservation of combinatorial structures in evolution scenarios. In: Lagergren, J. (ed.) RECOMB-WS 2004. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3388, pp. 1–14. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Bergeron, A., Mixtacki, J., Stoye, J.: Reversal distance without hurdles and fortresses. In: Sahinalp, S.C., Muthukrishnan, S.M., Dogrusoz, U. (eds.) CPM 2004. LNCS, vol. 3109, pp. 388–399. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Blin, G., Rizzi, R.: Conserved interval distance computation between non-trivial genomes. In: Wang, L. (ed.) COCOON 2005. LNCS, vol. 3595, pp. 22–31. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Bowers, J.E., Abbey, C., Anderson, A., Chang, C., Draye, X., Hoppe, A.H., Jessup, R., Lemke, C., Lennington, J., Li, Z.K., Lin, Y.R., Liu, S.C., Luo, L.J., Marler, B., Ming, R.G., Mitchell, S.E., Qiang, D., Reischmann, K., Schulze, S.R., Skinner, D.N., Wang, Y.W., Kresovich, S., Schertz, K.F., Paterson, A.H.: A high-density genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites for Sorghum, as a framework for comparative structural and evolutionary genomics of tropical grains and grasses. Genetics (2003)
Figeac, M., Varré, J.S.: Sorting by reversals with common intervals. In: Jonassen, I., Kim, J. (eds.) WABI 2004. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3240, pp. 26–37. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Floyd, R.W.: Algorithm 97: Shortest path. Communications of the ACM (1962)
Gale, M.D., Devos, K.M.: Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 95, 1971–1974 (1998)
Garey, M., Johnson, D.: Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York (1979)
Hannenhalli, S., Pevzner, P.A.: Transforming cabbage into turnip (polynomial algorithm for sorting signed permutations by reversals). Journal of the ACM 48, 1–27 (1999)
Jackson, B.N., Aluru, S., Schnable, P.S.: Consensus genetic maps: a graph theory approach. In: IEEE Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference (CSB 2005), pp. 35–43 (2005)
Keller, B., Feuillet, C.: Colinearity and gene density in grass genomes. Trends Plant Sci. 5, 246–251 (2000)
Lander, S.E., Green, P., Abrahamson, J., Barlow, A., Daly, M.J., et al.: MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1, 174–181 (1987)
Menz, M.A., Klein, R.R., Mullet, J.E., Obert, J.A., Unruh, N.C., Klein, P.E.: A High-Density Genetic Map of Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench Based on 2926 Aflp, Rflp and Ssr Markers. Plant Molecular Biology (2002)
Pevzner, P.A., Tesler, G.: Human and mouse genomic sequences reveal extensive breakpoint reuse in mammalian evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7672–7677 (2003)
Polacco, M.L., Coe, Jr., E.: IBM neighbors: a consensus GeneticMap (2002)
Sankoff, D., Zheng, C., Lenert, A.: Reversals of fortune. In: McLysaght, A., Huson, D.H. (eds.) RECOMB 2005. LNCS (LNBI), vol. 3678, pp. 131–141. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Yap, I.V., Schneider, D., Kleinberg, J., Matthews, D., Cartinhour, S., McCouch, S.R.: A graph-theoretic approach to comparing and integrating genetic, physical and sequence-based maps. Genetics 165, 2235–2247 (2003)
Zheng, C., Lenert, A., Sankoff, D.: Reversal distance for partially ordered genomes. Bioinformatics 21 (in press, 2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Blin, G., Blais, E., Guillon, P., Blanchette, M., El-Mabrouk, N. (2006). Inferring Gene Orders from Gene Maps Using the Breakpoint Distance. In: Bourque, G., El-Mabrouk, N. (eds) Comparative Genomics. RCG 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4205. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11864127_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11864127_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-44529-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44530-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)