Abstract
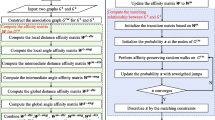
In this paper, we propose a novel stochastic attributed relational graph (SARG) matching algorithm in order to cope with possible distortions due to noise and occlusion. The support flow and the correspondence measure between nodes are defined and estimated by analyzing the distribution of the attribute vectors in the relation vector space. And then the candidate subgraphs are extracted and ordered according to the correspondence measure. Missing nodes for each candidates are identified by the iterative voting scheme through an error analysis, and then the final subgraph matching is carried out effectively by excluding them. Experimental results on the synthetic ARGs demonstrate that the proposed SARG matching algorithm is quite robust and efficient even in the noisy environment. Comparative evaluation results also show that it gives superior performance compared to other conventional graph matching approaches.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong, A.K.C., You, M.: Entropy and distance of random graphs with application to structural pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 7(5) (September 1985)
Sanfeliu, A., Alquézar, R., Andrade, J., Climent, J., Serratosa, F., Vergés, J.: Graph-based representations and techniques for image processing and image analysis. Pattern Recognition 35, 639–650 (2002)
Serratosa, F., Alquézar, R., Sanfeliu, A.: Function-described graphs for modelling objects represented by sets of attributes graphs. Pattern Recognition 36, 781–798 (2003)
Li, S.Z.: Matching: invariant to translations, rotations and scale changes. Pattern Recognition 25, 583–594 (1992)
Christmas, W.J., Kittler, J., Petrou, M.: Structural matching in computer vision using probabilistic relaxation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 17(8), 749–764 (1995)
Messmer, B.T., Bunke, H.: A new algorithm for error-tolerant subgraph isomorphism detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 20(5), 493–503 (1998)
Messmer, B.T., Bunke, H.: A decision tree approach to graph and subgraph isomorphism detection. Pattern Recognition 32, 1979–1998 (1999)
Gold, S., Rangarajan, A.: A graduated assignment algorithm for graph matching. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 18(4), 377–388 (1996)
Tsai, W.H., Fu, K.S.: Subgraph error-correcting isomorphisms for syntactic pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Systems Man and Cybernetics 13(1), 48–62 (1983)
El-Sonbaty, Y., Ismail, M.A.: A new algorithm for subgraph optimal isomorphism. Pattern Recognition 31(2), 205–218 (1998)
Herault, L., Horaud, R., Veillon, F., Niez, J.J.: Symbolic image matching by simulated annealing. In: Proc. British Machine Vision Conference, Oxford, pp. 319–324 (1990)
Krcmar, M., Dhawan, A.: Application of genetic algorithms in graph matching. In: Proc. Int’l. Conf. Neural Networks, vol. 6, pp. 3872–3876 (1994)
van Wyk, B.J., van Wyk, M.A.: The spherical approximation graph matching algorithm. In: Proc. Int’l. Workshop on Multidiscilinary Design Optimization, pp. 280–288 (August 2000)
van Wyk, B.J., Clark, J.: An algorithm for approximate least-squares attributed graph matching. In: Problems in Applied Mathematics and Computational Intelligence, pp. 67–72 (2000)
van Wyk, M.A., Durrani, T.S., van Wyk, B.J.: A RKHS interpolator-based graph matching algorithm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 24(7), 988–995 (2002)
van Wyk, B.J., van Wyk, M.A.: Kronecker product graph matching. Pattern Recognition 36, 2019–2030 (2003)
Nevatia, R., Babu, K.R.: Line extraction and description. Computer Graphics and Image Processing 13(1), 250–269 (1980)
Park, B.G., Lee, K.M., Lee, S.U., Lee, J.H.: Recognition of partially occluded objects using probabilistic ARG-based matching. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 90(3), 217–241 (2003)
Kim, D.H., Yun, I.D., Lee, S.U.: A new attributed relational graph matching algorithm using the nested structure of earth mover’s distance. In: Proceedings of IEEE International conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, pp. 48–51 (August 2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Park, B.G., Lee, K.M., Lee, S.U. (2006). A Novel Stochastic Attributed Relational Graph Matching Based on Relation Vector Space Analysis. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Philips, W., Popescu, D., Scheunders, P. (eds) Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. ACIVS 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4179. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11864349_89
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11864349_89
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-44630-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44632-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)