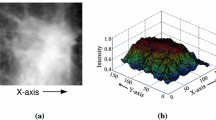
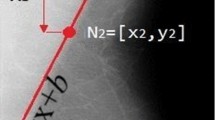
Abstract
A major problem that researchers face when working with digital medical images is that not all the information about the image is stored with it. Image analysis is used to extract useful information from the images. A clear problem when analyzing digital mammograms is that there is not a direct method to interpret pixel values. In this paper a method is presented that, performs the estimation of the amount of glandular tissue in digital mammograms. This contribution also shows how this knowledge about the pixels allows performing a segmentation of the breast region in its constituent parts; and if present, microcalcifications may be detected.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisano, E.D., et al.: Image processing algorithms for digital mammography: a pictorial essay. RadioGraphics 20, 1479–1491 (2000)
Li, H., et al.: Computerized radiographic mass detection - part I: lesion site selection by morphological enhancement and contextual segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20/4, 289–301 (2001)
Lasztovicza, L., et al.: Hybrid microcalcification detection in mammograms. In: Proceedings of the 17th International EURASIP Conference, BIOSIGNAL 2004, Brno, Czech Republic (June 2004)
Beuville, E., et al.: High resolution mammography using a scanned slit silicon strip detector. In: Karssemeijer, N., Thijssen, M., Hendriks, J., van Erning, L. (eds.) Digital Mammography; the 4th International Workshop on Digital Mammography, IWDM 1998, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, pp. 27–30. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1998)
National Electrical Manufacturers Association. PS 3.1-2004 Digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM). Part 1: introduction and overview (2004)
Wolfe, J.N.: Breast patterns as an index of risk for developing breast cancer. J Roentgenol 126(6), 1130–1137 (1976)
Highnam, R., Brady, M.: Mammographic image analysis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1999)
Karssemeijer, et al.: Volumetric breast tissue estimation from full-field digital mammograms. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 25(3), 273–282 (2006)
Krebs in Deutschland. 4. überarbeitete, aktualisierte Ausgabe. Arbeitsgemeinschaft Bevölkerungsbezogener Krebsregister in Deutschland. Saarbrücken (2004) ISBN 3-9808880-2-9
Aichinger, H., Dierker, J., Joite-Barfuss, S.: Radiation exposure and image quality in X-ray diagnostic radiology. Physical principles and clinical applications (published, 2004) ISBN: 3540442871
National Electrical Manufacturers Association. PS 3.10-2004 Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM). Part 10: Media Storage and File Format for Data Interchange (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Roller, D., Lampasona, C. (2006). A Method for Interpreting Pixel Grey Levels in Digital Mammography. In: Campilho, A., Kamel, M. (eds) Image Analysis and Recognition. ICIAR 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4142. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11867661_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11867661_52
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-44894-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44896-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)