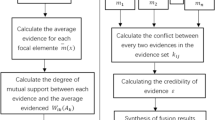
Abstract
D-S evidence theory has been studied and used for information fusion for a while. Though D-S evidence theory can deal with uncertainty reasoning from imprecise and uncertain information by combining cumulative evidences for changing prior opinions using new evidences. False evidence generated by any fault sensor will result in evidence conflict increasing and inaccurate fused results. Evidence relationship matrix proposed in this paper depicts the relationship among evidences. False evidences can be identified through the analysis of relationships among evidences. Basic probability assignments related to the false evidences may be decreased accordingly. The accuracy of information fusion may be improved. Case studies show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shafer, G.: A Mathematical Theory of Evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1976)
Fabre, S., Appriou, A., Briottet, X.: Presentation and Description of Two Classification Methods using Data Fusion based on Sensor Management. Information Fusion 2, 49–71 (2001)
Rottensteiner, F., Trinder, J., Clode, S., Kubik, K.: Using the Dempster - Shafer Method for the Fusion of LIDAR Data and Multi - Spectral Images for Building Detection. Information Fusion 6, 283–300 (2005)
Basir, O., Karray, F., Zhu, H.: Connectionist-Based Dempster–Shafer Evidential Reasoning for Data Fusion. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 6, 1513–1530 (2005)
Fan, X., Huang, H., Miao, Q.: Agent-based Diagnosis of Slurry Pumps Using Information Fusion. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensing, Computing and Automation. ICSCA 2006, Chongqing, China, May 8-11, pp. 1687–1691 (2006)
Fan, X., Zuo, M.J.: Fault Diagnosis of Machines based on D-S Evidence Theory. Part 1: D-S Evidence Theory and Its Improvement. Pattern Recognition Letters 5, 366–376 (2006)
Huang, H.Z.: Fuzzy Multi-Objective Optimization Decision-Making of Reliability of Series System. Microelectronics and Reliability 3, 447–449 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fan, X., Huang, HZ., Miao, Q. (2006). Evidence Relationship Matrix and Its Application to D-S Evidence Theory for Information Fusion. In: Corchado, E., Yin, H., Botti, V., Fyfe, C. (eds) Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning – IDEAL 2006. IDEAL 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4224. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11875581_162
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11875581_162
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-45485-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45487-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)