Abstract
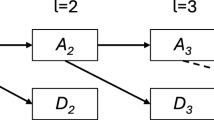
SB-Tree is a data structure proposed to represent time series according to the importance of the data points. Its advantages over traditional time series representation approaches include: representing time series directly in time domain (shape preservation), retrieving time series data according to the importance of the data points and facilitating multi-resolution time series retrieval. Based on these benefits, one may find this representation particularly attractive in financial time series domain and the corresponding data mining tasks, i.e. categorization and clustering. In this paper, an investigation on the size of the SB-Tree is reported. Two SB-Tree optimization approaches are proposed to reduce the size of the SB-Tree while the overall shape of the time series can be preserved. As demonstrated by various experiments, the proposed approach is suitable for different categorization and clustering applications.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, T.C., Chung, F.L., Luk, R., Ng, C.M.: A specialized binary tree for financial time series representation. In: The 10th ACM SIGKDD Workshop on Temporal Data Mining, pp. 96–104 (2004)
Geurts, P.: Pattern Extraction for Time Series Classification. In: Siebes, A., De Raedt, L. (eds.) PKDD 2001. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2168, pp. 115–127. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Smyth, P., Keogh, E.: Clustering and mode classification of engineering time series data. In: Proc. of the 3rd Int.l Conf. on KDD, pp. 24–30 (1997)
Keogh, E., Pazzani, M.: An enhanced representation of time series which allows fast and accurate classification, clustering and relevance feedback. In: Proc. of the 4th Int. Conf. on KDD, pp. 239–341 (1998)
Abonyi, J., Feil, B., Nemeth, S., Arva, P.: Principal component analysis based time se-ries segmentation - Application to hierarchical clustering for multivariate process data. In: Proc, of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Computational Cybernetics, pp. 29–31 (2003)
Lin, J., Vlachos, M., Keogh, E., Gunopulos, D.: Iterative Incremental Clustering of Time Series. In: Bertino, E., Christodoulakis, S., Plexousakis, D., Christophides, V., Koubarakis, M., Böhm, K., Ferrari, E. (eds.) EDBT 2004. LNCS, vol. 2992, pp. 106–122. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Ratanamahatana, C.A., Keogh, E., Bagnall, A.J., Lonardi, S.: A novel bit level time se-ries representation with implications for similarity search and clustering. Technical Report, UCR, TR-2004-93 (2004)
Xiong, Y., Yeung, D.Y.: Mixtures of ARMA models for model-based time series clustering. In: Proc. of ICDM, pp. 717–720 (2002)
Kalpakis, K., Gada, D., Puttagunta, V.: Distance measures for effective clustering of ARIMA time-series. In: Proc. of ICDM, pp. 273–280 (2001)
Chung, F.L., Fu, T.C., Luk, R., Ng, V.: Flexible Time Series Pattern Matching Based on Perceptually Important Points. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Workshop on Learning from Temporal and Spatial Data, pp. 1–7 (2001)
Keogh, E., Chakrabarti, K., Pazzani, M., Mehrotra, S.: Dimensionality reduction for fast similarity search in large time series databases. JKIS, 263–286 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Fu, Tc., Law, Cw., Chan, Kk., Chung, Fl., Ng, Cm. (2006). Stock Time Series Categorization and Clustering Via SB-Tree Optimization. In: Wang, L., Jiao, L., Shi, G., Li, X., Liu, J. (eds) Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery. FSKD 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4223. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11881599_141
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11881599_141
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-45916-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45917-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)