Abstract
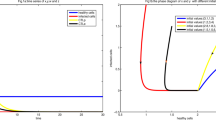
Physiological experiments demonstrate establishment of immunological tolerance is controlled by dose-timing and dose-amount of an antigen. My previous study reproduced the tolerance dependent on dose-timing of an antigen in a two Bcell clones network model with an “asymmetric” Bcell-Bcell interaction. This study first clarifies its mechanism using a dynamical system technique:nullcline analysis. Next, this study proposes a three Bcell clones network model with the same style of Bcell-Bcell interaction, and shows the model simulation can reproduce the tolerance dependent on dose-amount of an antigen: high and low zone tolerance. The success of this reproduction is worthy of attention. Because theoretical studies based on the traditional “symmetric” immune network modeling scheme have not been able to reproduce it well. This study would teach us the renewed recognition of “asymmetric” immune network modeling scheme.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hilliard, B., Ventura, E.S., Rostami, A.: Effect of timing of intravenous administration of myelin basic protein on the induction of tolerance in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Multiple Sclerosis 5, 2–9 (1999)
Elgert, K.D.: Immunology - Understanding the Immune System, p. 261. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York (1996)
Jerne, N.K.: Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann. Immunol 125C, 373–389 (1974)
Hoffmann, G.W.: Regulation of Immune Response Dynamics. In: DeLisi, C., Hiernaux, J.R.J. (eds.), vol. 1, pp. 137–162 (1982)
De Boer, R.J., Hogeweg, P.: Memory but no suppression in low-dimensional symmetric idiotypic network. Bull. Math. Biol. 51, 223–246 (1989)
Neumann, A.U., Weisbuch, G.: Window automata analysis of population dynamics in the immune system. Bull. Math. Biol. 54, 21–44 (1992)
Carneiro, J., Couthinho, A., Faro, J., Stewart, J.: A model of the immune network with B-T cell co-operation I. J. Theor. Biol. 182, 513–530 (1996)
Harada, K.: Emergence of Immune Memory and Tolerance in an Asymmetric Idiotype Network. In: Proc. of Ninth International Conference on Knowledge-based Intelligent Information Engineering Systems, vol. 2, pp. 61–71. Springer, Berlin (2005)
David, A.H., Wang, A.-L., Pawlak, L., Nisonoff, A.: Suppression of Idiotype Specificities in Adult Mice by Administration of Antiidiotypic Antibody. J. Exp. Med. 135, 1293–1300 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Harada, K. (2006). Tolerance Dependent on Timing/Amount of Antigen-Dose in an Asymmetric Idiotypic Network. In: Gabrys, B., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L.C. (eds) Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems. KES 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 4252. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11893004_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11893004_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-46537-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46539-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)