Abstract
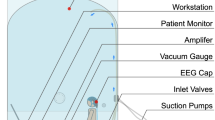
This paper presents an experiment to recognize early hypoxia based on EEG analyses. A chaotic neural network, the KIII model, initially designed to model olfactory neural systems is utilized for pattern classification. The experimental results show that the EEG pattern can be detected remarkably at an early stage of hypoxia for individuals.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saroj, K.L.L., Ashley, C.: A critical review of the psychophysiology of driver fatigue. Biological Psychology 55, 173–194 (2001)
Vuckovic, A., Andrew, R.V., Chen, C.N., Popovic, D.: Automatic recognition of alertness and drowsiness from EEG by an artificial neural network. Medical Engineering & Physics 24, 349–360 (2002)
Zhang, X.S., Rob, J.: EEG complexity as a measure of depth of anesthesia for patients. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 48, 12 (2001)
Kozma, R., Freeman, W.J.: Chaotic Resonance - Methods and Applications for Robust Classification of Noisy and Variable Patterns. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos. 11(6), 1607–1629 (2001)
Li, G., Lou, Z., Wang, L., Li, X., Freeman, W.J.: Application of Chaotic Neural Model Based on Olfactory System on Pattern Recognitions. In: Wang, L., Chen, K., S. Ong, Y. (eds.) ICNC 2005. LNCS, vol. 3610, pp. 378–381. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Quarder, S., Claussnitzer, U., Otto, M.: Using Singular-Value Decompositions to Classify Spatial Patterns Generated by a Nonlinear Dynamic Model of the Olfactory System. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 59, 45–51 (2001)
Hu, M., Li, J.J., Li, G., Tang, X.W., Freeman, W.J.: Normal and Hypoxia EEG Recog-nition Based on a Chaotic Olfactory Model. In: Wang, J., Yi, Z., Żurada, J.M., Lu, B.-L., Yin, H. (eds.) ISNN 2006. LNCS, vol. 3973, pp. 554–559. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Chang, H.J., Freeman, W.J.: Optimization of Olfactory Model in Software to Give 1/f Power Spectra Reveals Numerical Instabilities in Solutions Governed by Aperiodic (Chaotic) Attractors. Neural Networks 11, 449–466 (1998)
Chang, H.J., Freeman, W.J., Burke, B.C.: Biologically Modeled Noise Stabilizing Neuro-dynamics for Pattern Recognition. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos. 8(2), 321–345 (1998)
Freeman, W.J., Chang, H.J., Burke, B.C., Rose, P.A., Badler, J.: Taming Chaos: Stabilization of Aperiodic Attractors by Noise. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems 44, 989–996 (1997)
Principe, J.C., Tavares, V.G., Harris, J.G., Freeman, W.J.: Design and Implementation of a Biologically Realistic Olfactory Cortex in Analog VLSI. Proceedings of the IEEE 89(7), 1030–1051 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hu, M., Li, J., Li, G., Freeman, W.J. (2006). Analysis of Early Hypoxia EEG Based on a Novel Chaotic Neural Network. In: King, I., Wang, J., Chan, LW., Wang, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4232. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-46479-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46480-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)