Abstract
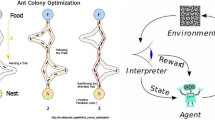
Online reinforcement learning achieves learning after update estimation value for (state, action) pairs selecting in present state before do state transition by next state. Therefore, online reinforcement learning needs polynomial search time to find most optimal value-function. But, a lots of reinforcement learning that are proposed for online reinforcement learning update estimation value for (state, action) pairs that agents select in present state, and because estimation value for unselected (state, action) pairs is evaluated in other episodes, perfect online reinforcement learning is not. Therefore, in this paper, we propose online ant reinforcement learning method using Ant-Q and eligibility trace to solve this problem. The eligibility trace is one of the basic mechanisms in reinforcement learning to handle delayed reward. The traces are said to indicate the degree to which each state is eligible for undergoing learning changes should a reinforcing event occur. Formally, there are two kinds of eligibility traces(accumulating trace or replacing traces). In this paper, we propose online ant reinforcement learning algorithms using an eligibility traces which is called replace-trace methods. This method is a hybrid of Ant-Q and eligibility traces. Although replacing traces are only slightly different from accumulating traces, it can produce a significant improvement in optimization. We could know through an experiment that proposed reinforcement learning method converges faster to optimal solution than Ant Colony System and Ant-Q.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colorni, A., Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V.: An Investigation of Some Properties of an Ant Algorithm. In: Manner, R., Manderick, B. (eds.) Proceedings of the Parallel Problem Solving from Nature Conference, pp. 509–520. Elsevier Publishing, Amsterdam (1992)
Colorni, A., Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V.: Distributed Optimization by Ant Colonies. In: Varela, F., Bourgine, P. (eds.) Proceedings of the First European Conference of Artificial Life, pp. 134–144. Elsevier Publishing, Amsterdam (1991)
Watkins, C.J.C.H.: Learning from Delayed Rewards. Ph.D. Thesis, King’s College, Cambridge, U.K (1989)
Fiecher, C.N.: Efficient Reinforcement Learning. In: Proceedings of the Seventh Annual ACM Conference on Computational Learning Theory, pp. 88–97 (1994)
Barnald, E.: Temporal-Difference Methods and Markov Model. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man and Cybernetics 23, 357–365 (1993)
Gambardella, L.M., Dorigo, M.: Solving Symmetric and Asymmetric TSPs by Ant Colonies. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference of Evolutionary Computation, pp. 622–627. IEEE Press, Los Alamitos (1996)
Gambardella, L.M., Dorigo, M.: Ant-Q: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to the Traveling Salesman Problem. In: Prieditis, A., Russell, S. (eds.) Proceedings of ML-95, Twelfth International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 252–260. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1995)
Dorigo, M., Gambardella, L.M.: A Study of Some Properties of Ant-Q. In: Ebeling, W., Rechenberg, I., Voigt, H.-M., Schwefel, H.-P. (eds.) PPSN 1996. LNCS, vol. 1141, pp. 656–665. Springer, Heidelberg (1996)
Dorigo, M., Maniezzo, V., Colorni, A.: The Ant System: Optimization by a Colony of Cooperation Agents. IEEE Trans. Systems, Man and Cybernetics-Part B 26(1), 29–41 (1996)
Stutzle, T., Hoos, H.: The Ant System and Local Search for the Traveling Salesman Problem. In: Proceedings of IEEE 4th International Conference of Evolutionary (1997)
Gambardella, L.M., Dorigo, M.: Ant Colony System: A Cooperative Learning Approach to the Traveling Salesman Problem. IEEE Trans. Evolutionary Computation 1(1) (1997)
Stutzle, T., Dorigo, M.: ACO Algorithms for the Traveling Salesman Problem. In: Miettinen, K., Makela, M., Neittaanmaki, P., Periaux, J. (eds.) Evolutionary Algorithms in Engineering and Computer Science. Wiley, Chichester (1999)
Sutton, R., Barto, A.: Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998)
Lee, S.G.: Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Algorithm Using Temporal Difference Error. In: Wang, J., Liao, X.-F., Yi, Z. (eds.) ISNN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3496, pp. 627–633. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
Lee, S.G., Chung, T.C.: A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm Using Temporal Difference Error in Ant Model. In: Cabestany, J., Prieto, A.G., Sandoval, F. (eds.) IWANN 2005. LNCS, vol. 3512, pp. 217–224. Springer, Heidelberg (2005)
http://www.iwr.uni-heidelberg.de/groups/comopt/software/TSPLIB95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lee, S. (2006). A Cooperation Online Reinforcement Learning Approach in Ant-Q. In: King, I., Wang, J., Chan, LW., Wang, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4232. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_54
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-46479-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46480-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)