Abstract
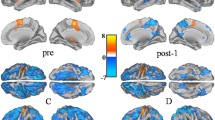
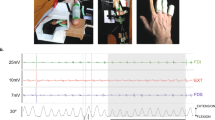
Based on a preliminary case study, we conducted an event related potentials (ERPs) research to explore the relationship between repetitive finger tapping and brain electrophysiological potentials. This present study found that the errors increased with motor repetitions during tapping tasks by right hand especially in the third stage. We defined this stage as the fatigue stage and the first stage as the initial stage. In the fatigue stage, the decreased N1 amplitudes (30-80 ms) with the right fronto-central and right central electrodes (FC4 and C4) were observed, while comparing with the initial stage. Moreover, the pronounced P2 amplitude (150-200 ms) and increased signal with time on right hemisphere (F4 and C4 electrodes) under fatigue state were noticed. Conversely, the contralateral left electrodes (FC3, C3, and F3) did not show aforementioned N1 and P2 differences between two stages. After using the Frequency Extraction method, a clear lateralized pattern in the fatigue stage was found. The left hemisphere showed lower and the right hemisphere showed higher alpha frequency phase content evolution. It was concluded that fatigue did lower the involvement of some areas in the brain but also did make right hemisphere take on more workload during the tapping task with right hand. We call this compensatory change as “fatigue-induced asymmetric hemispheric plasticity”. Besides, less signal change between two hemispheres in the fatigue stage was also found. Therefore, the mechanism of transcallosal interaction is strongly related to the fatigue state induced by the motor repetitions.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halder, P., Sterr, A., Brem, S., Bucher, K., Kollias, S., Brandeis, D.: Electrophysiological evidence for cortical plasticity with movement repetition. European Journal of Neuroscience 21(8), 2271–2277 (2005)
Peltier, S.J., Laconte, S.M., Niyazov, D.M., Liu, J.Z., Sahgal, V., Yue, G.H., Hu, X.P.: Reductions in interhemispheric motor cortex functional connectivity after muscle fatigue. Brain Research 1057(1-2), 10–16 (2005)
Boksem, M.A., Meijman, T.F., Lorist, M.M.: Effects of mental fatigue on attention: An ERP study. Cognitive Brain Research 25(1), 107–116 (2005)
Lorist, M.M., Klein, M., Nieuwenhuis, S., De Jong, R., Mulder, G., Meijman, T.F.: Mental fatigue and task control: planning and preparation. Psychophysiology 37(5), 614–625 (2000)
Benwell, N.M., Byrnes, M.L., Mastaglia, F.L., Thickbroom, G.: Primary sensorimotor cortex activation with task-performance after fatiguing hand exercise. Experimental Brain Research 21, 1–5 (2005)
Edgley, S.A., Winter, A.P.: Different effects of fatiguing exercise on corticospinal and transcallosal excitability in human hand area motor cortex. Experimental Brain Research 159(4), 530–536 (2004)
Howard, M.F., Reggia, J.: The effects of multi-task learning and time-varying hemispheric asymmetry on lateralisation in a neural network model. Laterality 9(2), 113–131 (2004)
Knyazeva, M., Koeda, T., Nijokiktjien, C., Jonkman, E.J., Kurganskaya, M., de Sonneville, L., Vildavsky, V.: EEG coherence changes during finger tapping in acallosal and normal children: A study of inter- and intrahemispheric connectivity. Behavioural Brain Research 89(1-2), 243–258 (1997)
Song, Y., Ding, Y., Fan, S., Qu, Z., Xu, L., Lu, C.: Neural substrates of visual perceptual learning of simple and complex stimuli. Clinical Neurophysiology 116(3), 632–639 (2005)
Smith, D.P., Hillman, C.H., Duley, A.R.: Influences of age on emotional reactivity during picture processing. The Journal of Gerontology: Psychological Science and Social Science 60(1), P49–P56 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Meng, LF., Lu, CP., Chen, BW., Chen, CH. (2006). Fatigue-Induced Reversed Hemispheric Plasticity During Motor Repetitions: A Brain Electrophysiological Study. In: King, I., Wang, J., Chan, LW., Wang, D. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4232. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11893028_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-46479-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46480-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)