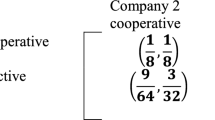
Abstract
In this research, an agent-based simulation model for price competition in oligopolies is built and Genetic Algorithm is used to evolve the oligopolies’ decisions of price while facing the competitors in markets. The experimental results show two factors influencing the price competition situations and ‘given’ factor that competitor can not control leads strong influence on their decision of price. Total cooperation (Collusion to high prices) seems not to be achieved under the different parameter settings while many competitors involving in the market and a limitation of cooperation forms in which no effect forces the achievement of total cooperation.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alchia, A.: Uncertainty Evolution and Economic Theory. Journal of Political Economics 58, 211–221 (1950)
Axelroad, R.: The Evolution of Cooperation, Penguin Books (1990)
Chen, S.-H., Ni, C.-C.: Simulating the Ecology of Oligopolistc Competition with Genetic Algorithms. Knowledge and Information Systems 2, 285–309 (2000)
Colman, A.M.: Game Theory and Experimental Games. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1982)
Holland, J.: Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems, University of Michigan, 2nd edn. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Yao, X., Darwen, P.J.: An Experimental Study of N-person Iterated Prisoners’ Dilemma Game. Informatica 18, 435–450 (1994)
Wang, T.D., Fyfe, C., Marney, J.P.: A Comparison of an Oligopoly Game and the N-iterated Prisoner’s Dilemma. In: The Fifth International Conference of the Society for Computational Economics (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, TD., Fyfe, C. (2006). Simulation of Cooperation for Price Competition in Oligopolies. In: Wang, TD., et al. Simulated Evolution and Learning. SEAL 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4247. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11903697_90
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11903697_90
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-47331-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-47332-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)