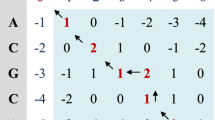
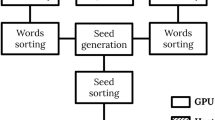
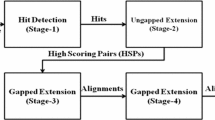
Abstract
Molecular Biologists frequently compute multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) to identify similar regions in protein families. However, aligning hundreds of sequences by popular MSA tools such as ClustalW requires several hours on sequential computers. Due to the rapid growth of biological sequence databases biologists have to compute MSAs in a far shorter time. In this paper we present a new approach to reduce this runtime using graphics processing units (GPUs). To derive an efficient mapping onto this type of architecture, we have reformulated the computationally most expensive part of ClustalW in terms of computer graphics primitives. This results in a high-speed implementation with significant runtime savings on a commodity graphics card.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, T., Waterman, M.: Identification of common molecular subsequences. Journal of Molecular Biology 147, 195–197 (1981)
Feng, D.F., Doolittle, R.F.: Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to a correct phylogenetic trees. Journal of Molecular Evolution 25, 351–360 (1987)
Thompson, J., Higgins, D., Gibson, T.: Clustalw: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994)
Heringa, J.: Two strategies for sequence comparison: Profile-preprocessed and secondary structure-induced multiple alignment. Comput. Chem. 23, 341–364 (1999)
Edgar, R.C.: Muscle: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797 (2004)
Notredame, C., Higgins, D., Heringa, J.: T-coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. Journal of Molecular Biology 302, 205–217 (2000)
Li, K.: Clustalw-mpi: Clustalw analysis using parallel and distributed computing. Bioinformatics 19, 1585–1586 (2003)
Ebedes, J., Datta, A.: Multiple sequence alignment in parallel on a workstation cluster. Bioinformatics 20, 1193–1195 (2004)
Mikhailov, D., Cofer, H., Gomperts, R.: Performance optimization of clustalw: parallel clustalw, ht clustal, and multiclustal. White papers, Silicon Graphics (2001)
Oliver, T., Schmidt, B., Nathan, D., Clemens, R., Maskell, D.: Using reconfigurable hardware to accelerate multiple sequence alignment with clustalw. Bioinformatics 21, 3431–3432 (2005)
Saitou, N., Nei, M.: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425 (1987)
Krüger, J., Westermann, R.: Linear algebra operators for gpu implementation of numerical algorithms. ACM Trans. Graph 22, 908–916 (2003)
Xu, F., Mueller, K.: Ultra-fast 3d filtered backprojection on commodity graphics hardware. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2004 (2004)
Horn, D., Houston, M., Hanrahan, P.: Clawhmmer: a streaming hmmer-search implementation. In: Proceedings of Supercomputing 2005 (2005)
Liu, W., Schmidt, B., Voss, G., Schröder, A., Müller-Wittig, W.: Bio-sequence database scanning on a gpu. In: Proceedings of 20th IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium (HICOMB Workshop) (2006)
Manocha, D.: General-purpose computations using graphics processors. Computer 38(8), 85–88 (2005)
Owens, J.D., Luebke, D., Govindaraju, N., Harris, M., Kruger, J., Lefohn, A.E., Purcell, T.: A survey of general-purpose computation on graphics hardware. In: Eurographics 2005, pp. 21–51 (2005)
Kessenich, J., Baldwin, D., Rost, R.: The opengl shading language, document revision 59. Technical report, http://www.opengl.org/documentation/oglsl.html (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Liu, W., Schmidt, B., Voss, G., Müller-Wittig, W. (2006). GPU-ClustalW: Using Graphics Hardware to Accelerate Multiple Sequence Alignment. In: Robert, Y., Parashar, M., Badrinath, R., Prasanna, V.K. (eds) High Performance Computing - HiPC 2006. HiPC 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4297. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11945918_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11945918_37
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-68039-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-68040-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)