Abstract
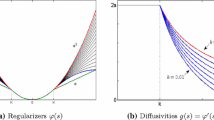
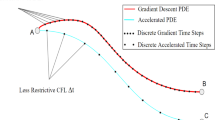
This article is concerned with new strategies with which explicit time-stepping procedures of PDE-based restoration models converge with a similar efficiency to implicit algorithms. Conventional explicit algorithms often require hundreds of iterations to converge. In order to overcome the difficulty and to further improve image quality, the article introduces new spatially variable constraint term and timestep size, as a method of nonflat time evolution (MONTE). It has been verified that the explicit time-stepping scheme incorporating MONTE converges in only 4-15 iterations for all restoration examples we have tested. It has proved more effective than the additive operator splitting (AOS) method in both computation time and image quality (measured in PSNR), for most cases. Since the explicit MONTE procedure is efficient in computer memory, requiring only twice the image size, it can be applied particularly for huge data sets with a great efficiency in computer memory as well.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12, 629–639 (1990)
Alvarez, L., Lions, P., Morel, M.: Image selective smoothing and edge detection by nonlinear diffusion. II. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29, 845–866 (1992)
Catte, F., Lions, P., Morel, M., Coll, T.: Image selective smoothing and edge detection by nonlinear diffusion. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29, 182–193 (1992)
Kim, S.: PDE-based image restoration: A hybrid model and color image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 15, 1163–1170 (2006)
Kim, S., Lim, H.: A non-convex diffusion model for simultaneous image denoising and edge enhancement. Electronic Journal of Differential Equations (accepted, 2006)
Marquina, A., Osher, S.: Explicit algorithms for a new time dependent model based on level set motion for nonlinear deblurring and noise removal. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22, 387–405 (2000)
Nitzberg, M., Shiota, T.: Nonlinear image filtering with edge and corner enhancement. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14, 826–833 (1992)
Rudin, L., Osher, S., Fatemi, E.: Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D 60, 259–268 (1992)
You, Y.L., Xu, W., Tannenbaum, A., Kaveh, M.: Behavioral analysis of anisotropic diffusion in image processing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 5, 1539–1553 (1996)
Chan, T., Shen, J.: Image Processing and Analysis. SIAM, Philadelphia (2005)
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer, New York (2003)
Sapiro, G.: Geometric partial differential equations and image analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Weickert, J., ter Haar Romeny, B., Viergever, M.: Efficient and reliable schemes for nonlinear diffusion filtering. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 7, 398–410 (1998)
Douglas Jr., J., Gunn, J.: A general formulation of alternating direction methods Part I. Parabolic and hyperbolic problems. Numer. Math. 6, 428–453 (1964)
Douglas Jr., J., Kim, S.: Improved accuracy for locally one-dimensional methods for parabolic equations. Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences 11, 1563–1579 (2001)
Cha, Y., Kim, S.: Edge-forming methods for image zooming. J. Mathematical Imaging and Vision (in press, 2006)
Cha, Y., Kim, S.: Edge-forming methods for color image zooming. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15, 2315–2323 (2006)
Kim, S., Kwon, S.H.: Efficiency and reliability in nonlinear diffusion filtering (in preparation)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kim, S., Kwon, SH. (2006). Explicit Nonflat Time Evolution for PDE-Based Image Restoration. In: Kalra, P.K., Peleg, S. (eds) Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 4338. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11949619_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11949619_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-68301-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-68302-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)