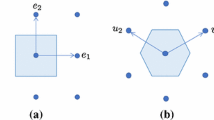
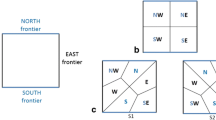
Summary
This paper describes an approach to smooth the surface and improve the quality of quadrilateral/hexahedral meshes with feature preserved using geometric flow. For quadrilateral surface meshes, the surface diffusion flow is selected to remove noise by relocating vertices in the normal direction, and the aspect ratio is improved with feature preserved by adjusting vertex positions in the tangent direction. For hexahedral meshes, besides the surface vertex movement in the normal and tangent directions, interior vertices are relocated to improve the aspect ratio. Our method has the properties of noise removal, feature preservation and quality improvement of quadrilateral/hexahedral meshes, and it is especially suitable for biomolecular meshes because the surface diffusion flow preserves sphere accurately if the initial surface is close to a sphere. Several demonstration examples are provided from a wide variety of application domains. Some extracted meshes have been extensively used in finite element simulations.
http://www.ices.utexas.edu/~jessica/paper/quadhexgf
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Baker. Identification and preservation of surface features. In 13th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 299–310, 2004.
F. J. Bossen and P. S. Heckbert. A pliant method for anisotropic mesh generation. In 5th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 63–76, 1996.
C. Bajaj, J. Warren, and G. Xu. A subdivision scheme for hexahedral meshes. The Visual Computer, 18(5-6):343–356, 2002.
C. Charalambous and A. Conn. An efficient method to solve the minimax problem directly. SIAM Journal of Numerical Analysis, 15(1):162–187, 1978.
S. Canann, J. Tristano, and M. Staten. An approach to combined laplacian and optimization-based smoothing for triangular, quadrilateral and quad-dominant meshes. In 7th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 479–494, 1998.
J. Escher, U. F. Mayer, and G. Simonett. The surface diffusion flow for immersed hypersurfaces. SIAM Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 29(6):1419–1433, 1998.
D. Field. Laplacian smoothing and delaunay triangulations. Communications in Applied Numerical Methods, 4:709–712, 1988.
L. Freitag and C. Ollivier-Gooch. Tetrahedral mesh improvement using swapping and smoothing. International Journal Numerical Methathemical Engineeringg, 40:3979–4002, 1997.
L. Freitag and P. Plassmann. Local optimization-based simplicial mesh untangling and improvement. International Journal for Numerical Method in Engineering, 49:109–125, 2000.
L. Freitag. On combining laplacian and optimization-based mesh smoothing techniqes. AMD-Vol. 220 Trends in Unstructured Mesh Generation, pages 37–43, 1997.
P. L. George and H. Borouchaki. Delaunay Triangulation and Meshing, Application to Finite Elements. 1998.
R. V. Garimella, M. J. Shashkov, and P. M. Knupp. Optimization of surface mesh quality using local parametrization. In 11th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 41–52, 2002.
P. Kinney. Cleanup: Improving quadrilateral finite element meshes. In 6th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 437–447, 1997.
C. Kober and M. Matthias. Hexahedral mesh generation for the simulation of the human mandible. In 9th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 423–434, 2000.
P. Knupp. Winslow smoothing on two dimensional unstructured meshes. Engineering with Computers, 15:263–268, 1999.
P. Knupp. Achieving finite element mesh quality via optimization of the jacobian matrix norm and associated quantities. part i-a framework for surface mesh optimization. International Journal Numerical Methathemical Engineeringg, 48:401–420, 2000.
P. Knupp. Achieving finite element mesh quality via optimization of the jacobian matrix norm and associated quantities. part ii-a framework for volume mesh optimization and the condition number of the jacobian matrix. International Journal Numerical Methathemical Engineeringg, 48:1165–1185, 2000.
R. Lohner, K. Morgan, and O. C. Zienkiewicz. Adaptive grid refinement for compressible euler equations. Accuracy Estimates and Adaptive Refinements in Finite Element Computations, I. Babuska et. al. eds. Wiley, pages 281–297, 1986.
M. Meyer, M. Desbrun, P. Schröder, and A. Burr. Discrete differential-geometry operators for triangulated 2-manifolds. VisMath’02, Berlin, 2002.
S. Mitchell and T. Tautges. Pillowing doublets: Refining a mesh to ensure that faces share at most one edge. In 4th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 231–240, 1995.
A. Oddy, J. Goldak, M. McDill, and M. Bibby. A distortion metric for isoparametric finite elements. Transactions of CSME, No. 38-CSME-32, Accession No. 2161, 1988.
S. Owen. A survey of unstructured mesh generation technology. In 7th Internat. Meshing Roundtable, pages 26–28, 1998.
G. Sapiro. Geometric Partial Differential Equations and Image Analysis. Cambridge, University Press, 2001.
M. Staten and S. Canann. Post refinement element shape improvement for quadrilateral meshes. AMD-Trends in Unstructured Mesh Generation, 220:9–16, 1997.
R. Schneiders. Refining quadrilateral and hexahedral element meshes. In 5th International Conference on Grid Generation in Computational Field Simulations, pages 679–688, 1996.
I. B. Semenova, V. V. Savchenko, and I. Hagiwara. Two techniques to improve mesh quality and preserve surface characteristics. In 13th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 277–288, 2004.
S. M. Shontz and S. A. Vavasis. A mesh warping algorithm based on weighted laplacian smoothing. In 12th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 147–158, 2003.
K. Shimada, A. Yamada, and T. Itoh. Anisotropic triangular meshing of parametric surfces via close packing of ellipsoidal bubbles. In 6th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 375–390, 1997.
S.-H. Teng and C. W. Wong. Unstructured mesh generation: Theory, practice, and perspectives. International Journal of Computational Geometry and Applications, 10(3):227–266, 2000.
T. J. Willmore. Riemannian geometry. Clareden Press, Oxford, 1993.
G. Xu, Q. Pan, and C. Bajaj. Discrete surface modelling using partial differential equations. Accepted by Computer Aided Geomtric Design, 2005.
G. Xu. Discrete laplace-beltrami operators and their convergence. CAGD, 21:767–784, 2004.
Y. Zhang and C. Bajaj. Adaptive and quality quadrilateral/hexahedral meshing from volumetric data. In 13th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 365–376, 2004.
Y. Zhang and C. Bajaj. Adaptive and quality quadrilateral/hexahedral meshing from volumetric data. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering (CMAME), in press, www.ices.utexas.edu/~jessica/paper/quadhex, 2005.
Y. Zhang, C. Bajaj, and B-S Sohn. 3d finite element meshing from imaging data. Special issue of Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering on Unstructured Mesh Generation, in press, 2004.
T. Zhou and K. Shimada. An angle-based approach to two-dimensional mesh smoothing. In 9th International Meshing Roundtable, pages 373–384, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Bajaj, C., Xu, G. (2005). Surface Smoothing and Quality Improvement of Quadrilateral/Hexahedral Meshes with Geometric Flow. In: Hanks, B.W. (eds) Proceedings of the 14th International Meshing Roundtable. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-29090-7_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-29090-7_27
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-25137-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-29090-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)