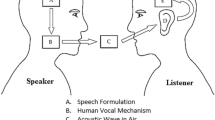
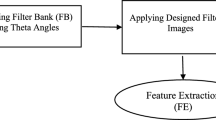
Abstract
Progress of automatic speech recognition systems’ (ASR) development is, inter alia, made by using signal representation sensitive for more and more sophisticated features. This paper is an overview of our investigation of the new context-sensitive speech signal’s representation, based on wavelet-Fourier transform (WFT), and proposal of it’s quality measures. The paper is divided into 5 sections, introducing as follows: phonetic-acoustic contextuality in speech, basics of WFT, WFT speech signal feature space, feature space quality measures and finally conclusion of our achievements.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Benitez C., Burget L. et al. (2001) Robust ASR front-end using spectral-based and discriminant features: experiments on the Aurora tasks. Eurospeech, Aalborg
2. Bojar B. (1974) Elementy jêzykoznawstwa dla informatyków. PAN ODiIN, Warszawa.
3. Bölla K., Foldi E. (1987) A Phonetic Conspectus of Polish, The Articulatory and Acoustic Features of Polish Speech Sounds. Linguistic Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Budapest
4. Chang S., Greenberg S.,Wester M. (2001) An Elitist Approach to Articulatory- Acoustic Feature Classification. Eurospeech, Aalborg
5. Dukiewicz L., Piela R. (1962) Wyrazistoćæ I rozróźnialnoćæ gòsek w jêzyku polskim w zaleęnoćci od górnej granicy czêstotliwoćcifi Przeglą Telekomunikacyjny
6. Dukiewicz L. (1995) Gramatyka Wspólczesnego Jêzyka Polskiego—Fonetyka. Instytut Jêzyka Polskiego PAN, Kraków
7. Galka J., Kêpiński M. (2004) Wavelet-Fourier Spectrum Parameterisation for Speech Signal Recognition. Proceedings of the Tenth National Conference on Application of Mathematics in Biology and Medicine. wiêty Krzyź
8. Gold B., Morgan N. (2000) Speech and Audio Signal Processing. John Wiley&Sons Inc.
9. Jassem W. (1966) The Distinctwe Features and Entropy of the Polish Phoneme System. Biuletyn PTJ XXIV
10. Jassem W. (1973) Podstawy fonetyki akustycznej. PWN, Warszawa
11. Kêpiński M. (2001) Ulepszona metodaćledzenia punktów charakterystycznych. II Krajowa Konferencja Metody i Systemy Komputerowe w badaniach naukowych i projektowaniu inźynierskim, Kraków
12. Kòsowski P. (2000) Usprawnienie procesu rozpoznawania mowy w oparciu o fonetykêi fonologiêjêzyka polskiego. Politechnika lś ka, Gliwice
13. Martens P. J. (Chairman) (2000) Continuous Speech Recognition over the Telephone, Electronics&Information Systems (ELIS). Final Report of COST Action 249, Ghent University
14. Miêkisz M., Denenfeld J. (1975) Phonology and Distribution of Phonemes in Present-day English and Polish. Ossolineum, Wrolcaw
15. Rabiner L., Juang B. H. (1993) Fundamentals of Speech Recognition. Prentice- Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
16. Rolcawski B. (1976) Zarys fonologii, fonetyki, fonotaktyki i fonostatystyki wspólczesnego jêzyka polskiego. Gdańsk
17. SAMPA—A computer readable phonetic alphabet. http://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/home/sampa/home.htm
18. Sharma S., Ellis D. et al. (2000) Feature extraction using non-linear transformation for robust speech recognition on the Aurora database. ICASSP, Istanbul
19. Shuangyu C. (2002) A Syllable, Articulatory-Feature, and Stress-Accent Model of Speech Recognition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley
20. Somervuo P. (2003) Experiments With Linear And Nonlinear Feature Transformations In HMM Based Phone Recognition. ICASSP, Hong Kong
21. Somervuo P., Chen B., Zhu Q. (2003) Feature Transformations and Combinations for Improving ASR Performance. Eurospeech, Geneva
22. Tadeusiewicz R., Flasiński M. (2000) Rozpoznawanie obrazów. AGH, Kraków
23. Tadeusiewicz R. (1988) Sygnal mowy. Wydawnictwa Komunikacji i Łącznoćci, Warszawa
24. Tan B., Lang R. et al. (1994) Applying wavelet analysis to speech segmentation and classification. Proceedings of Spie the International Society for Optical Engineering, Orlando, 750–761
25. Tyagi V., McCowan ifi et al. (2003) Mel-cepstrum Modulation Spectrum (MCMS) Features for Robust ASR. Dalle Molle Institute for Perceptual Arti ficial Intelligence (IDIAP)
26. Xiong Z., Huang T. S. (2002) Boosting Speech/Non-Speech Classification Using Averaged Mel-frequency Cepstrum Coef-ficients Features. Proceedings of The Third IEEE Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia
27. Ziólko M., Kêpiński M., Galka J. (2003) Wavelet-Fourier Analysis of Speech Signal. Procedings of the Workshop on Multimedia Communications and Services, Kielce
28. Ziólko M., Stêpień J. (1999) Does the Wavelet Transfer Function Exist? Proceedings of the ECMCS99, CD ROM, Kraków
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gałka, J., Kępiński, M. (2006). WFT – Context-Sensitive Speech Signal Representation. In: Kłopotek, M.A., Wierzchoń, S.T., Trojanowski, K. (eds) Intelligent Information Processing and Web Mining. Advances in Soft Computing, vol 35. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-33521-8_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-33521-8_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-33520-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-33521-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)