Abstract
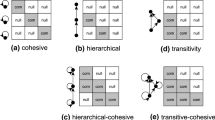
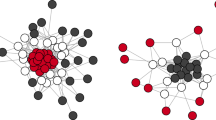
This paper provides an introduction to the blockmodeling problem of how to cluster networks, based solely on the structural information contained in the relational ties, and a brief overview of generalized blockmodeling as an approach for solving this problem. Following a formal statement of the core of generalized blockmodeling, a listing of the advantages of adopting this approach to partitioning networks is provided. These advantages, together with some of the disadvantages of this approach, in its current state, form the basis for proposing some open problem sets for generalized blockmodeling. Providing solutions to these problem sets will transform generalized blockmodeling into an even more powerful approach for clustering networks of relations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAKER, W. E. (1986): Three-dimensional blockmodeling. Journal of Mathematical Sociology,12, 191–223.
BATAGELJ, V., DOREIAN, P. and FERLIGOJ, A. (2006): Three dimensional blockmodeling. International Sunbelt XXVI Social Network Conference, Vancouver, Canada, April 25–30.
BATAGELJ, V., DOREIAN, P. and FERLIGOJ, A. (1992a): An optimization approach to regular equivalence. Social Networks, 14, 121–135.
BATAGELJ, V., FERLIGOJ, A. and DOREIAN, P. (1992b): Direct and indirect methods for structural equivalence. Social Networks, 14, 63–90.
BATAGELJ, V. and MRVAR, A. (1998): Pajek — Program for large network analysis. Connections, 21(2), 47–57. See also http://vlado.fmf.unilj.si/pub/networks/pajek for documentation and the most recent version of this program.
BORGATTI, S. P. and EVERETT, M. (1989) The class of regular equivalences: Algebraic structure and computation. Social Networks, 11, 65–88.
BREIGER, R. L., BOORMAN, S. A. and ARABIE, P. (1975): An algorithm for clustering relational data with applications to social network analysis and comparison to multidimensional scaling. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 12, 328–383.
BURT, R. S. (1976): Positions in networks. Social Forces, 55, 93–122.
DAVIS J. A. and LEINHARDT, S. (1972): The structure of positive interpersonal relations in small groups. In: J. Berger, M. Zelditch Jr and B. Anderson (Eds) Sociological Theories in Progress, Volume 2. Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 218–251.
DOREIAN, P.(1993): A measure of standing for citation networks within a wider environment. Information Processing and Management, 30/1, 21–31.
DOREIAN, P., BATAGELJ, V. and FERLIGOJ, A. (2005): Generalized Blockmodeling. University of Cambridge, New York.
DOREIAN, P., BATAGELJ, V. and FERLIGOJ, A. (2000): Symmetric-Acyclic Decompositions of Networks. Journal of Classification, 17/1, 3–28.
DOREIAN, P., BATAGELJ, V. and FERLIGOJ, A. (1994): Partitioning networks based on generalized concepts of equivalence. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 19, 1–27.
DOREIAN, P. and MRVAR A. (1996): A partitioning approach to structural balance. Social Networks, 18, 149–168.
DOREIAN, P. and STOKMAN, F. N. (Eds.) (1997): Social Network Evolution Gordon and Breach, New York.
DOREIAN, P. and WOODARD, K. L. (1994): Defining and locating cores and boundaries of social networks. Social Networks, 16, 267–293.
HEIDER, F. (1946): Attitudes and cognitive organization Journal of Psychology, 21, 107–112.
HUMMON, N. P. and CARLEY, K (1993) Social networks as normal science Social Networks, 15, 71–106.
LAUMANN E. O., MARSDEN, P., V. and PRENSKY, D. (1983): The boundary specification problem in network analysis. In: R. S. Burt and M. J. Minor (Eds) Applied Network Analysis: A Methodological Introduction Sage, Beverly Hills, 18–34.
LORRAIN, F. and WHITE, H. C. (1971): Structural equivalence of individuals in social networks. Journal of Mathematical Sociology, 1, 49–80.
SAILER, L. D. (1978): Structural equivalence: Meaning and definition, computation and application. Social Networks, 1, 73–90.
WHITE, D. R. and REITZ, K. P. (1983): Graph and semigroup homomorphisms on networks of relations. Social Networks, 5, 193–234
WINSHIP, C. and MANDEL, M (1983): Roles and positions: A critique and extension of the blockmodeling approach. In S. Leinhardt (Ed.) Sociological Methodology 1983–4 Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, 314–344.
ŽIBERNA, A. (2005): Generalized blockmodeling of valued networks. University of Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin · Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Doreian, P. (2006). Some Open Problem Sets for Generalized Blockmodeling. In: Batagelj, V., Bock, HH., Ferligoj, A., Žiberna, A. (eds) Data Science and Classification. Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg . https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-34416-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-34416-0_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-34415-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-34416-2
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)