Abstract
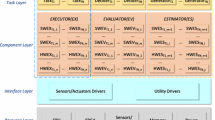
In this study, the implementation of a previously proposed robotic replanning framework is presented. The proposed framework integrates a high level replanning paradigm into a three layer robotic architecture. There has been a great deal of studies on managing unexpected events at lower two levels of three layer architectures but doing replanning at highest level still needs investigation. Supporting replanning with real-time vision feedback from working environment and integrating a learning mechanism as a basis increases the success ratio.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkin, R. C., “Behaviour-Based Robotics”, The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1999.
Gat, E., 1998, “Three Layer Architectures”, in Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Robots, MIT Press.
Laird, E. L., Congdon, C. B., and Coulter, K. J., 1998, “The Soar User’s Manual Version 8.2”, University of Michigan.
Veloso, M. M., Carbonell, J., P’erez, M. A, Borrajo, D., Fink, E., and Blythe, J., 1995, “Integrating planning and learning: The Prodigy architecture”, Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 7(1), pp. 81–120.
Koening, S. and Simmons, R. G., “Xavier: A Robot Navigation Architecture Based on Partially Observable Markov Decision Process Models”., in: Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Robots, D. Kortenkamp, R.P. Bonasso, R. Murphy (eds.), MIT Press, 1998.
Yildirim, S. and Tunali, T., “A new methodology for dealing with uncertainty in robotic tasks”, XIV. Int. Symp. on Comp.& Inf.Sci., Kusadasi, TURKIYE.
Haigh, K. Z., 1998, “Situation-Dependent Learning for Interleaved Planning and Robot Execution”, Ph.D thesis, CMU.
Pryor, L., & Collins, G., 1996, “Planning for Contingencies: A Decision_based Approach”, Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 4, pp. 287–339.
Newell, A. and Simon, H. (1963). GPS: A program that simulates human thought. In Computers and Thought, ed. Feigenbaum and Feldman. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yildirim, S., Tunali, T. (2002). The Implementation of a Robotic Replanning Framework. In: Yakhno, T. (eds) Advances in Information Systems. ADVIS 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2457. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36077-8_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36077-8_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-00009-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36077-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive