Abstract
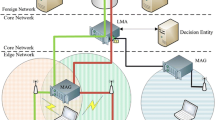
The Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) provides a signaling mechanism for end-to-end QoS in Integrated Services Internet. Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a fast label-based switching technique that can offer new QoS capabilities for large scale IP networks. In this paper, in order to obtain more efficient use of scarce wireless bandwidth, increase data rate and reduce QoS signaling delay and data packet delay during handoff in Mobile IPv6, we propose a novel scheme that improves the efficiency using a Hierarchical Mobile Agents Tree (HMAT) based on the definition of new option called QoS Object Option (QOO) over MPLS. The HMAT can be chosen and configured in any way as the network administrator thinks appropriate. The QOO is included in the hop-by-hop extension header of certain packets that carry Binding messages. Mobile agents are required to manage QOO, resource reservation and other mobility related tasks on behalf of mobile hosts. The root mobile agent of the HMAT is also an edge Label Switch Router (LSR) in the MPLS Core Network. This paper defines the efficient signaling and control mechanisms to support QoS in Access and Core Network for Mobile IPv6.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Perkins, “ IP Mobility Support, ” RFC 2002, October 1996.
D.B. Johnson and C. Perkins, “ Mobility Support in IPv6, ” IETF Internet-Draft, work in progress, November 2000.
E. Rosen, “Multiprotocol Label Switching Architecture, ” RFC3031, January 2001.
R. Braden, L. Zhang, S. Berson, S. Herzog, and S. Jamin, “ Resource ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP) Version 1 Functional Specification, ” RFC 2205, September 1997.
J. Wrclawski, “ The Use of RSVP with IETF Integrated Services, ” RFC 2210, September 1997.
A. Terzis, J. Krawczyk, J. Wroclawski, L. Zhang, “ RSVP Operation Over IP Tunnels, ” RFC 2746, January 2000.
A.K. Talukdar, B.R. Badrinath, and A. Acharya, “ MRSVP: A Reservation Protocol for an Integrated Services packet Network with Mobile Hosts, ” Tech. Rep. Dcs-tr-337, Department of Computer Science, Rutgers University, U.S.A., 1997.
I. Mahadevan and K.M. Sivalingam, “ An Experimental Architecture for providing QoS guarantees in Mobile Networks using RSVP, ” IEEE PIMRC, Boston, September 1998.
A. Terzis and M. Srivastava and L. Zhang, “ A Simple QoS Signaling Protocol for Mobile Hosts in the Integrated Services Internet, ” INFOCOM 1999.
W. Chen and L. Huang, “ RSVP Mobility Support: A Signaling Protocol for Integrated Services internet with Mobile Hosts, ” INFOCOM 2000.
Qi. Shen and W. Seah and A. Lo, “ Flow Transparent Mobility and QoS Support for IPv6-based Wireless Real-time Services, ” IETF Internet-Draft, work in progress, February 2001.
H. Chaskar and R. Koodli, “ A Framework for QoS Support in Mobile IPv6, ” IETF Internet-Draft, work in progress, March 2001.
Zhao Wei Qu, ChoongSeon Hong, “ QoS Provision Architecture for Mobile IP using RSVP, ” Proceedings of KICS National Conference, Vol. 23, pp. 1551, Cheju, Korea, July 2001.
Zhao Wei Qu, ChoongSeon Hong, “A QoS Provision Architecture for Mobile IPv6 Using RSVP, ” ICOIN16, January 2002.
D. Awduche, L. Berger, D. Gan, T. Li, V. Srinivasan, G. Swallow, “RSVP-TE: Extensions to RSVP for LSP Tunnels, ” RFC3209, December 2001.
D. Awduche, A. Hannan, X. Xiao, “ Applicability Statement for Wxtensions to RSVP for LSP-Tunnels, ” RFC3210, December 2001.
Zhong Ren, C.K. Tham, C.C. Foo, C.C. Ko, “Supporting MPLS in Mobile IP, ” ICT2000, May 2000.
J.K. Choi, M.H. Kim, Y.J. Lee, “Mobile IPv6 Support in MPLS Network, ” IETF Internet-Draft, work in progress, December 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qu, Z.W., Hong, C.S., Lee, S. (2002). A QoS Provision Architecture for Mobile IPv6 over MPLS Using HMAT. In: Shafazand, H., Tjoa, A.M. (eds) EurAsia-ICT 2002: Information and Communication Technology. EurAsia-ICT 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2510. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36087-5_67
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36087-5_67
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-00028-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36087-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive