Abstract
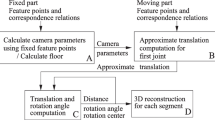
Motion estimation of articulated objects with two subparts from monocular images are studied in this paper for three cases: 1) one subpart translates, and the other one rotates around the joint; 2) the two rotation axes of the subparts are parallel to each other; 3) the two rotation axes of the subparts are perpendicular with each other. Three motion models are established respectively, and the conditions for a solution are discussed in detail, which shows that only 4, 5 and 6 image point correspondences are needed respectively for the three kinds of articulated motion estimation. The problem of how to distribute the points on the two subparts is also explained. Finally, a lot of simulated experiments are presented, validating the rightness and efficiency of our motion models.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jon A. Webb and J. K. Aggarwal, “Structure from motion of rigid and jointed motions”, Artificial Intelligence, vol. 19, pp107–130, 1982.
R. J. Holt, A. N. Netravali, T. S. Huang and R. J. Qian, “Determining articulated motion from perspective views: a decomposition approach”, Pattern Recognition, vol. 30, pp1435–1449, 1997.
Pan Chunhong, Chen Shen and Ma Songde, “Motion analysis of articulated objects and its application in human motion analysis”, Chinese Journal of Electronics, vol. 9, No. 1, pp76–81, Jan. 2000.
D. Sinclair and K. Zesar, “Further constraints on visual articulated motions”, Proc. On CVPR, pp94–99, 1996.
T.S. Huang and A.N. Netravali, “Motion and structure from feature correspondences: A review”, Proceeding of the IEEE, Vol. 82, No. 2, February, 1994, pp. 252–268.
H. C. Longuet-Higgins, “A computer program for reconstructing a scene from two projections”, Nature, vol. 293, pp133–135, Sept. 1981.
C. Bregler and J. Malik, “Tracking people with twist and exponential maps”, Proc. Conf. On CVPR, pp8–15, 1998.
H. Segawa, H. Shioya, N. Hiraki and T. Totsuka, “Constraint-conscious smoothing framework for the recovery of 3D articulated motion from image sequences”, Pro. 4th Int. Conf. On Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp476–482, 2000.
C. J. Taylor, “Reconstruction of Articulated Objects from Point Correspondences in a Single Uncalibrated Images”, Proc. Conf. On CVPR, vol. 1, pp677–684, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Huang, T.S. (2002). Motion Estimation of Articulated Objects from Perspective Views. In: Perales, F.J., Hancock, E.R. (eds) Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. AMDO 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2492. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36138-3_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36138-3_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-00149-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36138-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive