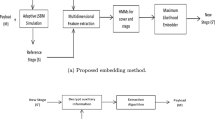
Abstract
Steganography and steganalysis of digital images is a cat-and-mouse game. In recent work, Fridrich, Goljan and Du introduced a method that is surprisingly accurate at determining if bitmap images that originated as JPEG files have been altered (and even specifying where and how they were altered), even if only a single bit has been changed. However, steganographic embeddings that encode embedded data in the JPEG coefficients are not detectable by their JPEG compatibility steganalysis. This paper describes a steganographic method that encodes the embedded data in the spatial domain, yet cannot be detected by their steganalysis mechanism. Furthermore, we claim that our method can also be used as a steganographic method on files stored in JPEG format. The method described herein uses a novel, topological approach to embedding. The paper also outlines some extensions to the proposed embedding method.
Research supported by the Office of Naval Research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Anderson. Stretching the limits of steganography. In R. Anderson, editor, Information Hiding 1996, volume LNCS 1174, pages 39–48. Springer, 1996. 258
R. Anderson. Security Engineering. Wiley, 2001. 272
J. Dugundji. Topology. Allyn and Bacon, 1976. 267
J. J. Eggers, R. Bäuml, and B. Girod. A communications approach to image steganography. In SPIE Electronic Imaging 2002, Security and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents IV, volume 4675, pages 26–37, San Jose, USA, Jan. 2002. 259
J. Fridrich. Methods for detecting changes in digital images. In 6th IEEE International Workshop on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS’98), Melbourne, Australia, 4-6 November 1998. 258
J. Fridrich, M. Goljan, and R. Du. Steganalysis based on JPEG compatibility. In A. Tescher, B. Vasudev, and Jr. V.M. Bove, editors, SPIE Vol. 4518, Special session on Theoretical and Practical Issues in Digital Watermarking and Data Hiding, SPIE Multimedia Systems and Applications IV, pages 275–280, Denver, CO, 20-24 August 1998.258, 260, 262
N. F. Johnson, Z. Duric, and S. Jajodia. Information hiding: Steganography and watermarking-attacks and countermeasures. In Advances in Information Security 1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2001. 258
E. Kawaguchi and R.O. Eason. The principle and applications of bpcssteganography. In SPIE International Symposium on Voice, Video, and Data Communications: Multimedia Systems and Applications, pages 464–473, Boston, MA, November 2-4 1998. 259, 265, 273
E. Kawaguchi and M. Niimi. Modeling digital image into informative and noiselike regions by complexity measure. In Information Modeling and Knowledge Bases IX, pages 255–265. IOS Press, April 1998. 273
C. Kurak and J. McHugh. A cautionary note on image downgrading. In Computer Security Applications Conference, pages 153–159, San Antonio, Dec. 1992. 258, 259
Y. Lee and L. Chen. An adaptive image steganographic model based on minimum-error lsb replacement. In Ninth National Conference on Information Security, pages 8–15, Taichung, Taiwan, 14-15 May 1999. 273
Y. Lee and L. Chen. A high capacity image steganographic model. In IEE Vision, Image and Signal Processing, 2000. 259
L. M. Marvel, C.G. Boncelet Jr., and C.T. Retter. Spread spectrum image steganography. IEEE Trans. Image Processing, 8:1075–1083, August 1999. 272
L. M. Marvel, G.W. Hartwig, and C. Boncelet. Compression-compatible fragile and semi-fragile tamper detection. In SPIE EI Photonics West, pages 131–139, San Jose, CA, 2000. 260
I. S. Moskowitz, L. Chang, and R.E. Newman. Capacity is the wrong paradigm. In New Security Paradigms Workshop, Virginia Beach, VA, USA, September 2002. 258, 259, 263
I. S. Moskowitz, N. F. Johnson, and M. Jacobs. A detection study of an NRL teganographic method. NRL Memorandum Report NRL/MR/5540-02-8635, Naval Research Laboratory, Code 5540, August 16 2002. 259
I. S. Moskowitz, G. E. Longdon, and L. Chang. A new paradigm hidden in steganography. In New Security Paradigms Workshop, pages 12–22, Ballycotton, County Cork, Ireland, Sept 2000. ACM (also appears in “The Privacy Papers” ed. R Herold, Auerbach Press 2002). 259
M. Niimi, H. Noda, and E. Kawaguchi. An image embedding in image by a complexity based region segmentation method. In ICIP, volume 3, pages 74–77, 1997. 273
W.B. Pennebaker and J. L. Mitchell. JPEG Still Image Data Compression Standard. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1993. 261
F.A.P. Petitcolas, R.J. Anderson, and M.G. Kuhn. Information hiding-a survey. Proceedings of the IEEE, 87(7):1062–1078, July 1999. 272
N. Provos. Defending against statistical steganalysis. In 10th USENIX Security Symposium, pages 323–335, August 2001. 258, 272
N. Provos. Probabilistic methods for improving information hiding. Technical Report 01-1, CITI, University of Michigan, January 2001. 258, 272
N. Provos and P. Honeyman. Detecting steganographic content on the internet. Technical Report 01-1, CITI, University of Michigan, August 2001. 258
G. Strang. The discrete cosine transform. SIAM Review, 41(1):135–147, 1999. 261
A. Westfeld. F5-a steganographic algorithm: High capacity despite better steganalysis. In S. Moskowitz(ed.) Information Hiding, LNCS 2137, IH 2001, pages 289–302. Springer, 2001. 270, 272
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Newman, R.E., Moskowitz, I.S., Chang, L., Brahmadesam, M.M. (2003). A Steganographic Embedding Undetectable by JPEG Compatibility Steganalysis. In: Petitcolas, F.A.P. (eds) Information Hiding. IH 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2578. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36415-3_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36415-3_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-00421-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36415-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive