Abstract
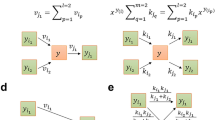
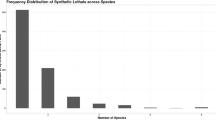
In this work we propose a quantitative definition of enzyme importance in a metabolic network. Using a graph analysis, we investigate the metabolism of the Escherichia coli to determine a relation between the damage generated on the metabolic network by the deletion of an enzyme and the experimentally determined viability of the organism in the absence of the enzyme. We predict that a large fraction (91%) of enzymes cause a small damage and have a low probability of lethality according to experimental results, while a small fraction of them (9%) cause a high damage and have a high probability of lethality. We obtain a quantitative correlation between damage and its probability of lethality. Our results may be a universal property of the metabolic network of other organisms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devos, D., Valencia, A.: Intrinsic Errors in Genome Annotation. Trends in Genetics. 17 (2001) 429–431. 142
Jeong, H., Tombor, B., Albert, R., Oltvai, Z. N., Barabási, A.-L.: The Large-Scale Organization of Metabolic Networks. Nature 407 (2000) 651–654. 143, 146, 147
Ravasz, E., Somera, A.L., Mongru, D.A., Oltvai, Z.N., Barabási, A.-L.: Hierarquical Organization of Modularity in Metabolic Networks. Science 297 (2002) 1551–1555. 143
Karp, P.D., Krummenacker, M., Paley, S., Wagg, J.: Integrated Pathway-Genome Databases and Their Role in Drug Discovery. Trends in Biotechnology 17 (1999) 275–281. 143
Jeong, H., Mason, S.P., Barabási, A.-L., Oltvai, Z. N.: Lethality and Centrality in Protein Networks. Nature 411 (2001) 41–42. 143, 146
Chartrand, G.: Introductory Graph Theory. Dover Publications, New York (1977). 144
Edwards, J. S., Ibarra, R.U., Palsson, B.O.: In silico Predictions of Escherichia coli Metabolic Capabilities are Consistent with Experimental Data. Nature Biotechnology 19 (2001) 125–130. (http://gcrg.ucsd.edu/downloads/index.html) 144
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S.: KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Research 28 (2000) 27–30. (http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/kegg2.html) 144
Overbeek, R. et al.: WIT: Integrated System for High-Throughput Genome Sequence Analysis and Metabolic Reconstruction. Nucleic Acids Research 28 (2000) 123–125. (http://ergo.integratedgenomics.com/ERGO/) 144
Ouzounis, C. A., Karp, P. D.: Global Properties of the Metabolic Map of Escherichia coli. Genome Research 10 (2000) 568–576. (http://BioCyc.org/ecocyc/) 144
Schroeder, E. K., de Souza, O.N., Santos, D. S., Blanchard, J. S., Basso, L.A.: Drugs that Inhibit Mycolic Acid Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 3 (2002) 197–225. 147
Campbell, J.W., Cronan, J. E. Jr.: Bacterial Fatty Acid Biosynthesis: Targets for Antibacterial Drug Discovery. Annu Rev. Microbiology 55 (2001) 305–332. 147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lemke, N., Herédia, F., Barcellos, C.K., Mombach, J.C.M. (2003). A Method to Identify Essential Enzymes in the Metabolism: Application to Escherichia Coli . In: Priami, C. (eds) Computational Methods in Systems Biology. CMSB 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2602. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36481-1_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36481-1_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-00605-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-36481-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive