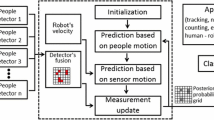
Abstract
In this paper two computationally efficient methods for building a map of the occupancy of a space based on measurements from a ring of ultrasonic sensors are presented. The first is a method based on building a histogram of the occurrence of free and occupied space. The second is based on the calculation of the rate between occupied space measurements with respect to the total. The resulting occupancy maps have been compared with those obtained with other well-known methods, bothcoun t as well as Bayes-rule-based ones, in static environments. Free space, occupied space and unknown labels were also compared subsequent to the application of a simple segmentation algorithm. The results obtained gave rise to statistically significant differences between all the different types on comparing the resulting maps. In the case of comparing occupancy labels, no differences were found between the following pairs of methods: RATE and SUM (p − value = 0.157), ELFES and RATE (p − value = 0.600) and ELFES and SUM (p − value = 0.593).
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks R.A. (1996) A robust layered controlfor a mobile robot IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, RA-2(1):14–23.
Borenstein, J. and Koren, Y. (1991) Histogramic in-motion mapping for mobile robot obstacle avoidance. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 7(4):535–539.
Duckett, T. and Nehmzow, U. (1998) Mobile robot self-localisation and measurement of performance in middle-scale environments. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 24:57–69.
Elfes, A. (1989) Occupancy grids: A Probabilistic Framework for Mobile Robot Perception and Navigation. PhD. thesis, Electrical and Computer Engineering. Dept./Robotics Inst. Carnegie Mellon Univ.
Elfes, A. (1989) Using Occupancy Grids for Mobile Robot Perception and Navigation. IEEE Computer Magazine, 22(6):46–57.
Gambino, F., Oriolo, G. and Ulivi, G. (1996) A comparison of three uncertainty calculus techniques for ultrasonic map building. SPIE Int. Symp. Aerospace/Defense sensing contr., Orlando, FL., pages 249–260.
Gasós, J. and Martín, A. (1997) Mobile robot localization using fuzzy maps. In Martin, T. and Ralescu, A., editors, Fuzzy Logic in Artificial Intelligence, 1188, Springer-Verlag, 207–224.
Iglesias, R., Regueiro, C.V., Correa, J. and Barro, S. (1998) Supervised Reinforcement Learning: Application to a Wall Following Behaviour in a Mobile Robot, In Pobil, A.P., Mira, J. and Ali, M., editors, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, 1416, Springer-Verlag, pages 300–309.
Iglesias, R., Regueiro, C.V., Correa, J. and Barro, S. (1997) Implementation of a Basic Reactive Behavior in Mobile Robotics Through Artificial Neural Networks, In Mira, J., Moreno-Diaz, R. and Cabestany, J., editors, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1240, Springer-Verlag, pages 1364–1373.
Koenig, S. and Simmons, R.G. (1998) Xavier: A Robot Navigation Architecture Based on Partially Observable Markov Decision Process Models In Kortenkamp, D., Bonasso, R.P. and Murphy, R., editors, Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Robots: Case Studies of Successful Robot Systems. AAAI Press / The MIT Press.
Konolige, K. (1996) A Refined Method for Occupancy Grid Interpretation. In Dorst, L., van Lambalgen, M., and Voorbraak, F., editors, Lecture Nores in Artificial Intelligence, 1093, Springer-Verlag, pages 338–352.
Kuipers, B.J. and Byun, Y.T., (1991) A robot exploration and mapping strategy based on a semantic hierarchy of spatial representations. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 8:47–63.
Mendenhall, W., Scheaffer, R.L. and Wackerly, D.D. (1986) Mathematical Statistics with Applications. Ed. PWS Publishers.
Nehmzow, U. and Smithers, T. (1991) Mapbuilding using Self-Organising Networks in Really Useful Robots In Meyer, J.A. and Wilson, S., editors, From Animals to Animats, Proc. 1st conference on Simulation on Adaptive Behavior, MIT Press.
Oriolo, G., Ulivi, G. and Vendittelli, M. (1998) Real-Time Map Building and Navigation for Autonomous Robots in Unknown Environments IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 28(3):316–333.
Pagac, D., Nebot, M. and Durrant-Whyte, H. (1998) An Evidential Approach to Map-Building for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 14(4).
Thrun, S. (1998) Learning Metric-Topological Maps for Indoor Mobile Robot Navigation. AI Journal, 99(1):21–71.
Yamauchi, B. and Beer, R. (1996) Spatial Learning for Navigation in Dynamic Environments IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 26(3):496–505.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Rodríguez, M., Correa, J., Iglesias, R., Regueiro, C.V., Barro, S. (2000). Probabilistic and Count Methods in Map Building for Autonomous Mobile Robots. In: Wyatt, J., Demiris, J. (eds) Advances in Robot Learning. EWLR 1999. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 1812. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-40044-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-40044-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-41162-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-40044-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive