Abstract
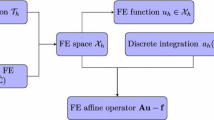
When designing high voltage equipment like power transformers, it is of essential importance to precisely and efficiently calculate eddy-current problems in a transformer to determine possible losses. A method suitable for such simulations is the Boundary-Element method (BEM) [2]. As far as the simulation is concerned, for electrical devices operating continuously under alternating current, time-harmonic states are of interest. These lead to an elliptic transmission problem for the eddy-current Maxwell equations. With some modifications, the linear equation system resulting from the boundary element discretization is well-conditioned. For realistic problems, however, the discretization leads to very large, non-symmetric systems of linear equations. To deal with such large equation systems, iterative solution techniques such as GMRES [9] must be employed. However, for certain combinations of materials occurring in electrical engineering (such as e.g. iron and copper parts) the parallel boundary integral equation system and its discretizations are ill-conditioned, primarily caused by the physical parameters in the problem formulation. In order to cope with such problems, the Seminar for Applied Mathematics at the ETH Zürich, Switzeland has developed a preconditioner for the eddy-current system of second kind Boundary Integral Equations [4] which has been integrated into the framework of the boundary element field simulation code POLOPT [1].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Andjelic. POLOPT 4.5 User’s Guide. ABB Corporate Research Center Heidelberg, 1996.
R. Bausinger and G. Kuhn. Die Boundary-Element Methode (in German). Expert Verlag, Ehingen, 1987.
N. Boden, D. Cohen, R. Felderman, J. Seizovic A. Kulawik, C. Seitz, and Wen-King Su. Myrinet: A Gigabit-per-Second Local Area Network. IEEE Micro, 15(1):29–36, February 1995.
G. Schmidlin, Ch. Schwab et al. Preconditioning second kind boundary integral equations for 3-d eddy current problems (unpublished). Technical report, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2000.
L. Huse, K. Omang, H. Bugge, H. Ry, A. Haugsdal, and E. Rustad. SCI: Scalable Coherent Interface. Architecture and Software for High-Performance Compute Clusters, volume 1734 of LNCS State-of-the-Art Survey, chapter 14, ScaMPI — Design and Implementation. Springer Verlag, October 1999. ISBN 3-540-66696-6.
IEEE Computer Society. IEEE Standard for the Scalable Coherent Interface (SCI). IEEE Std 1596-1992, 1993. IEEE 345 East 47th Street, New York, NY 10017-2394, USA.
I.D. Mayergoyz. Eddy current problems and the boundary integral equation method. Computational Electromagnetics, pages 163–171, 1996.
Message Passing Interface Forum (MPIF). MPI: A Message-Passing Interface Standard. Technical Report, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, June 1995. http://www.mpi-forum.org.
Y. Saad and M.H. Schultz. GMRES: A generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. In SI AM J.Sci. Stat. Comput., pages 856–869. 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Trinitis, C., Schulz, M., Eberl, M., Karl, W. (2001). SCI-Based LINUX PC-Clusters as a Platform for Electromagnetic Field Calculations. In: Malyshkin, V. (eds) Parallel Computing Technologies. PaCT 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2127. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44743-1_53
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44743-1_53
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42522-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44743-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive