Abstract
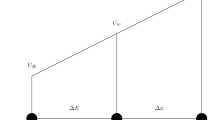
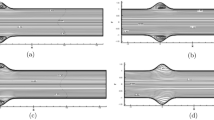
Surgical planning as a treatment for vascular diseases requires fast blood flow simulations that are efficient in handling changing geometry. It is, for example, necessary to try different paths of a planned by pass and study the resulting hemodynamic flow fields before deciding the final geometrical solution. With the aid of a real time interactive simulation environment that uses an efficient flow solver, this allows flexible treatment planning. In this article, we demonstrate that the lattice Boltzmann method can be an alternative robust CFD technique for such kind of applications. Steady flow in a 2D symmetric bifurcation is studied and the obtained flow fields and stress tensor components are compared to those obtained by a Navier-Stokes (NS) solver. We also demonstrate that the method is fully adaptive to interactively changing geometry.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Shear Stress
- Boltzmann Equation
- Lattice Boltzmann Method
- Dissipative Particle Dynam
- Lattice Boltzmann Model
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
References
Fung, Y. C.: Biomechanics: Circulation., 2nd edn. Springer-verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1997) 192; Wootton, D., Ku D. N.: Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 01 299 (1999); The World Health Report 2002, WHO publications (2002).
Goyen, M., Ladd, M. E., Debatin, J. F., Barkhausen, J., Truemmler, K. H., Bosk, S., Ruehm, S. G.: Dynamic 3D MR angiography of the pulmonary arteries in under four seconds. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 13 (2001) 372–377.
Foster, I. and Kesselmann, C. (eds.): The Grid: BluePrint for a new computing Infrastructure, Morgan Kaufmann, (1999).
Zhao, Z., Belleman, R. G., van Albada, G. D., Sloot, P. M. A., 2002: AG-IVE: an Agent based solution to constructing Interactive Simulation Systems. In: Computational Science-ICCS 2002, Proceedings Part I, in series Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2329., (2002) 693–703.
Belleman, R. G., Kaandorp, J. A., Sloot P. M. A.: A Virtual Environment for the Exploration of Diffusion and Flow Phenomena in Complex Geometries, Future Generation Computer Systems, 14 209–214 (1998).
Krafczyk, M., Cerrolaza, M., Schulz, M., Rank, E., 1998. Analysis of 3D transient blood flow passing through an artificial aortic valve by Lattice-Boltzmann methods. Journal of Biomechanics. 31 (1998) 453–462.
Ladd, A. J. C.: Numerical simulations of particulate suspensions via a discretized Boltzmann equation. Part I. Theoretical foundation. J. Fluid Mech. 271 285–309 (1994).
Sauro Succi: The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond. Oxford University Press (2001).
Benzi R., Succi S., Vergassola M.: The Lattice Boltzmann Equation-Theory and Applications. Phys. Rep. 222: 145–197 (1992); Chen S, Doolen GD: Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30: 329–364
Chopard B. and Droz M.: Cellular Automata modeling of Physical Systems. Cambridge University Press (1998).
Zou, Q., Hou, S., Chen S., Doolen, G. D.: An improved incompressible lattice Boltzmann model for time independent flows. J. Stat. Phys. 81 (1995) 35–48.
Maier, S. E., Meier, D., Boesiger, P., Moser, U., Viele A.: Human abddominal aorta: Comparative Measurements of blood flow with MR Imaging and Multigated Doppler US. Radiology, 171 (1989) 487–492.
Taylor, C. A., Hughes, T. J. R., Zarins, C. K.: Finite element modeling of blood flow in arteries. Comp. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 158 (1998) 155–196.
Berger, S. A., Jou, L-D.: Flows in stenotic vessels. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32 (2000) 347–382.
Reneman, R. S., Hoeks, A. P. G., van de Vosse, F. N., Ku, D. N.: Three-dimensional blood flow in bifurcations: computational and experimental analyses and clinical applications. Cerebrovascular Diseases. X (1993) 185–192.
Donald A. McDonald: Blood flow in arteries, Camelot Press, (1974).
Zou, Q., He, X: On pressure and velocity boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model. Phys. Fluids 9, (1997) 1591–1598.
Caro, C. G., Pedley, T. J., Schroter R. C., Seed, W. A.: The mechanics of the circulation. Oxford University Press, (1978).
FLUENT 4.5, Fluent Inc., http://www.fluent.com (1998).
Bernaschi M., Succi S., Chen H. D., Zhang R. Y.: International Journal of Modern Physics C 13 (2002): 675–687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Artoli, A.M., Kandhai, D., Hoefsloot, H.C.J., Hoekstra, A.G., Sloot, P.M.A. (2003). Lattice Boltzmann, a Robust and Accurate Solver for Interactive Computational Hemodynamics. In: Sloot, P.M.A., Abramson, D., Bogdanov, A.V., Dongarra, J.J., Zomaya, A.Y., Gorbachev, Y.E. (eds) Computational Science — ICCS 2003. ICCS 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2657. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44860-8_107
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44860-8_107
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-40194-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44860-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive